Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by poor insulin secretion or impaired insulin function both leading to hyperglycemia. One of the long-term complications of this disease process is neuropathy. Neuropathy, particularly in the extremities, leads to poor sensation, which contributes to the occurrence of ulcers typically observed on the feet of diabetic patients [1]. Current treatments for diabetic ulcers include wound dressing, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, negative pressure therapy [2-4], and in advanced cases, amputation of the limb.
An alternative treatment for diabetic foot ulcers is a matrix scaffold for new tissue generation, an acellular human dermal matrix (ADM) allograft as reviewed by Wainwright and Bury [5]. Decellularized human skin has been used for a variety of medical procedures, primarily involving wound healing, soft tissue reconstruction, and sports medicine applications [6-9].
Case 1
The following case presentation involves treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer with this human ADM, DermACELL®.
55 years old diabetic and hypertensive male patient and taking insulin for 8 years came to our center 7th of September 2015 with the history of two weeks swelling on the Right Big Toe. He received treatment from Health Center. Patient was admitted to BDF hospital where Surgical Debridement and Angioplasty done twice for the right L.L also Angioplasty for the left L.L. Upon examination, impending pedal pulses and good capillary circulation was noted. Wet gangrene on his Right Big Toe with edema of the foot was also noted. Patient was managed by Incision and Drainage and Right Big Toe Amputation done under ankle block on September 08, 2015. Culture was done. Antibiotic Tab Bactiflox 500 mg twice daily and tab Dalacin 300 mg thrice daily was started. A Blood investigation was done. Hba1c 7.9% Hb 10.9 g/dl, Wbc 9.2.
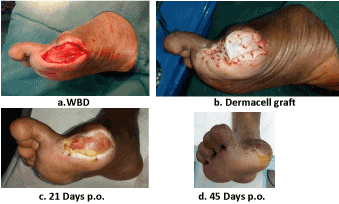
Figure 1a-1d. Case 1- Treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer with this human ADM
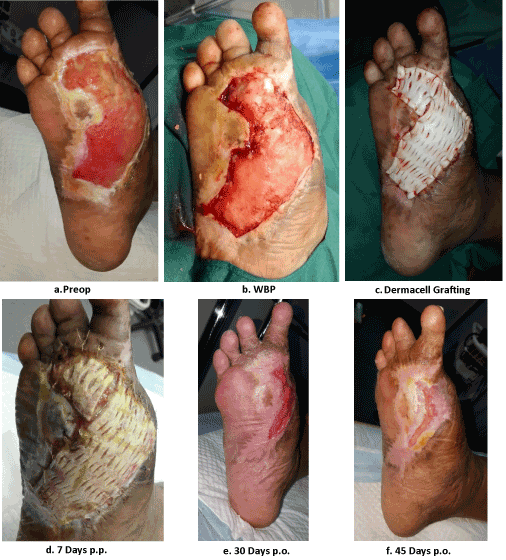
Figure 2a-2f. Case 2- Treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer with this human ADM
September 09, 2015, he started for his follow up dressing and debridement on his Right Big Toe amputated stump. On September 17, 2015 during his follow up dressing, clean granulating wound was noted, and the doctor stops his antibiotic. He is for culture for the next visit. Bactrim and Co-Amox was prescribed. He is coming twice a week in the clinic and is showing good improvement with less necrotic tissue. October 05, 2015 dressing on his right big toe stump, clean granulating wound and the doctor stops Dalacin and continue Ciprofloxacin. Culture was done. October 08, 2015 dressing on his right big toe shows improvement, for culture and Cephalexin was prescribed. Since October 12, 2015 until November 05, 2015 for his follow up dressing and debridement on his right big toe is improving and continue Cephalexin. On November 11, 2015 dressing and debridement on his right foot and urgent
Incision and Drainage was done for him. November 12, 2015 to December 30, 2015 during his follow up visits for dressing and debridement on his right foot with local Julmentin was given, and clean granulating wound. Dalacin C cap was prescribed. Steri strip was also applied.
January 04, 2016 follow up dressing on his right foot clean wound and prescribed Avalox. January 07, 2016 dressing and Skin grafting using Dermacell on his right foot to the granulating surface was done for him. Mesporin was also given.
January 14, 2016 upon his follow up visit for dressing right foot Post Dermacell there is failure of half the graft and intact lateral half. Four days after the failure of the graft, on January 18, 2016 wound is clean and the graft is accepting along the lateral half. On his follow up visit, January 23, 2016 to April 06, 2016 dressing on his right foot is improving, clean wound and graft. On April 13, 2016 upon his visit for dressing right foot, during assessment there is a small ulcer on his left big toe was noted. April 27, 2016 during his dressing on his right foot, it was near cured. And few days, he came back to our clinic for follow up dressing he was completely cured on May 07, 2016.
Case 2
The following case presentation involves treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer with this human ADM, DermACELL®.
This 65 years male patient who was diagnosed with DM in the year 1987 and he were under treatment of oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin on a daily basis. He had other medical conditions such as impaired Renal Failure and was a post CABG case. He was also a chronic smoker for about 10 years.
He presented to our center on August 31, 2015 with a very poor condition. He was febrile (39.4 celsius) with edematous right foot leg infected wound with a foul discharge odor. The cause of his wound was due to pulling of excess skin on the right big toe and became infected and treated in Health Center during dressing but did not improve.
Upon examination of the foot, there were palpable pedal pulses, pitting edema of the right foot and leg, gangrenous ulcer right big toe with spreading necrotizing fasciitis and suppuration till hind of the foot also blister formation of the foot. X-ray, arterial Doppler and blood investigation was done, and he underwent immediate Incision and Drainage with debridement of the right foot under ankle block.
He came next day for follow up post-op dressing and there was marked improvement of the foot, the edema was diminished and less cellulitis. His Doppler study revealed he need for vascular surgeon consultation and was given referral letter. He underwent successful angioplasty followed by amputation and debridement in BDF with NPWT applied and was removed after five days due to financial constraints. This patient continued to come for follow up dressing twice weekly. His wound was managed by dressing with debridement and antibiotics according to the pus culture continuity report.
Dermacell graft was applied to his right foot followed by application of below knee slop.
References
- Hozibal, Kimberly B and Wukich DK (2012) Diabetic foot infections: current concept review. Diabet Foot Ankle [Crossref]
- Dumville JC, Deshpande S, O'Meara S and Speak K (2011) Foam dressings for healing diabetic foot ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9: [Crossref]
- Gupta, Subhas, Barbara Bates-Jensen, Allen Gabriel, Allen Holloway, et al. (2007) Differentiating negative pressure wound therapy devices: an illustrative case series. Wounds 19:1-9.
- Zamboni WA, Wong HP, Stephenson LL and Pfeifer MA (1997) Evaluation for hyperbaric oxygen for diabetic wounds: a prospective study. Undersea Hyperb Med 24: 175-179. [Crossref]
- Wainwright DJ and Bury SB (2011) Acellular Dermal Matrix in the Management of the Burn Patient. Aesthet Surg J 31: 13S-23S. [Crossref]
- Wong I, Burns J and Snyder S (2010) Arthroscopic Graft Jacket Repair of Rotator Cuff Tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 19: 104-109. [Crossref]
- Wilkins R (2010) Acellular Dermal Graft Augmentation in Quadriceps Tendon Rupture Repair. Curr Orthop Pract 21: 315-319.
- Lee DK (2007) Achilles Tendon Repair with Acellular Tissue Graft Augmentation in Neglected Ruptures. J Foot Ankle Surg 46: 451-455. [Crossref]
- Sbitany H, Sandeen SN, Amalfi AN, Davenport MS and Langstein HN (2009) Acellular Dermis-Assisted Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction versus Complete Submuscular Coverage: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 124: 1735-1740. [Crossref]


