Abstract
Histological, histochemical, immunohistochemical and morphometric methods studied 12 consecutive identical twins with total villous shell, weighing 650 - 800 g and 12 consecutive singleton pregnancies weighing 450-550 g. Gestational age 39-40 weeks, for no pathology, no independent labor complications. Objective - histological analysis of the placenta villous membrane monochorionic identical human twins. The epithelium of the terminal villi of identical twins showed a high proliferative activity of Ki-67-positive nuclei (in singleton pregnancy rate is 3 times lower). Vascularization of the villi is carried angiogenesis mechanisms. Data obtained in the study suggest that placental villous tree monochorionic twins is characterized by incomplete human histogenesis of the main structural components of terminal villi.
Key words
identical twins, monochorionic placenta, terminal villi, proliferation Ki-67-positive nuclei
Introduction
The frequency of multiple pregnancy increases in recent decades due to the increase in the mother's age at the time of the birth of the child and the use of assisted reproductive technologies [1]. The proportion of monozygotic twins is 4 per 1000 genera [1], of which 20-30% have a common chorionic plate [2]. Monochorionic twins, in comparison with dichorionic ones, are distinguished by significant perinatal mortality (18-35%) [2]. Vascular placental anastomoses connect both fetuses through the chorion [3], which can cause a hemodynamic imbalance between them and lead to a significant risk of restriction of height and weight, aneuploidy, structural abnormalities of the fetus, placenta and umbilical cord [1,3]. Specific complications of multiple pregnancy are transfusion syndrome of twins and twin disappearance syndrome; intrauterine fetal death may lead to cerebral ischemia of the twin and subsequent neurologic impairment [3]. At the same time, in the available literature information on the histological structure of the chorionic plate of the human placenta with monotonous wins are few and scattered.
The aim of the work is a histological analysis of the villous shell of monochorionic placenta of monozygotic twins of a human.
Materials and methods
The material was obtained from the maternity hospitals of Yaroslavl in pregnancies that occurred without pathology and independent labor without complications. Pathomorphological research was carried out in the clinical hospital N.V. Solovyov, Yaroslavl. The study was approved by the ethical committee of the Yaroslavl State Medical University (protocol No. 41 of October 4, 2016). We studied 12 sequences with developing monotonous twins, who had their own umbilical cord; amnion, chorion and other membranes, including the placenta, were common. The gestation period is 39-40 weeks, the mass of the afterbirth is 650-800 g. As a comparison, the chorion of 12 stages was studied in a single pregnancy with a mass of 450-550 g. From the fetal membrane of the placenta excised fragments in the central, middle and marginal part, the material was fixed in 10% neutral formalin and liquid Carnoy. Serial sections 4-5 microns thick were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, according to McManus and Hart. The glycogen content was detected by a Schiff-iodic acid reaction (control with amylase). Immunohistochemical study was performed on dewaxed sections with an indirect immunoperoxidase method using the Ki-67 proliferation marker (Ventana, USA), followed by staining with Mayer's hematoxylin. The number of immunopositive nuclei and the determination of the proliferation index were performed on the immunohystoster of Roche Benchmark XT Ventana (USA). At the same time, 1000 nuclei were counted in the trophoblastic epithelium of intermediate, terminal villi (TV) and syncytial kidneys (SK), endothelium of capillaries and arteries, smooth myocytes of arteries TV. The outer diameter of the branches of the chorion arteries was measured with a screw-eyepiece micrometer MOV -1-15x (LOMO, Russia). The quantitative data were processed by the method of variational statistics. The significance of the differences was judged from the Student's t-value.
Resolutions and contiguity
The chorionic plate of identical twins is represented mainly by a dense network of terminal villi located in a wide intervorsing space. TV is well vascularized with 5-7 fetal capillaries (Figure 1a). Hemocapillaries are surrounded by a loose fibrous connective tissue and occupy a peripheral position under the trophoblastic epithelium. The epithelium of TV is flattened, on it numerous syncytial kidneys (SK) are formed, represented by clusters of syncytiotrophoblast (ST) nuclei (Figure 1a). Nucleated thin sections of the epithelium, which are in direct contact with fetal hemocapillaries, form syncytocapillary membranes.
Figure 1. Terminal nores of the monochorionic placenta of monozygotic twins of a human.
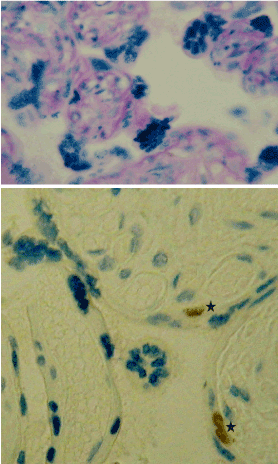
a - syncytial kidneys and hemocapillaries; b-immunoexpression of the Ki-67 marker (* - asterisk) in the cytotrophoblast.
Masson coloring (a); immunohistochemical reaction with anti-Ki-67 antibody with staining of Mayer's hematoxylin (b). Increase 300.
In the epithelium of TV monozygotic twins, high proliferative activity of Ki-67 positive nuclei were revealed (in single-pregnancy - 3 times lower) (table 1, Figure 1b). The epithelium of intermediate villi (IV) is characterized by an insignificant index of proliferation (in singleton pregnancy the marker gives a negative reaction). In S? the index of proliferation is reduced almost 4 times in comparison with the epithelium of TV, but 2 times exceeds the level of the index in single pregnancy.
Table 1. The index Ki67 of immunopositive nuclei in trophoblastic epithelium and blood vessels of intermediate and terminal villi chorionic villus in single and two-fetal pregnancy,% (x ± sx)
Group of observations |
Epithelium IV |
Epithelium TV |
Epithelium of syncytial kidneys |
Endothelium capillaries of TV |
Endothelial arteries TV |
Smooth myocytes of arteries TV |
singleton pregnancy |
– |
9,4 ± 1,5 |
3,3 ± 0,8 |
2,8 ± 0,4 |
0,9 ± 0,2 |
1,7 ± 0,2 |
bipartite pregnancy |
0,5 ± 0,1 |
28,2 ±3,3* |
7,2 ± 1,5* |
7,5 ± 1,1* |
1,8 ± 0,2* |
2,5 ± 0,3* |
Note: TV - terminal villi of the chorion; IV - intermediate villi of the chorion. Differences are significant: * at P <0.01
Arterial vessels of the chorionic plate of the placenta in single-pregnancy and monotonous twins have pronounced structural features: the middle shell is characterized by significant development and is represented by two layers of smooth mitsites: internal - obliquely-longitudinal and external - circular (Figure 2a). Tunica media contains a dense network of reticular and elastic fibrils, tunica externa is surrounded by intertwining bundles of collagen fibers (Figure 2b). Cytoplasm of smooth myocytes is characterized by a high content of glycogen. The diameter of the arteries varies from 60 to 120 microns. In single-pregnancy, the number of such vessels in the chorionic plate is almost 50% (47.3 ± 1.2), and for monozygotic twins it approaches 90% (89.1 ± 3.5, P <0.01).
Figure 2. Chorionic arteries of identical twins of a human.
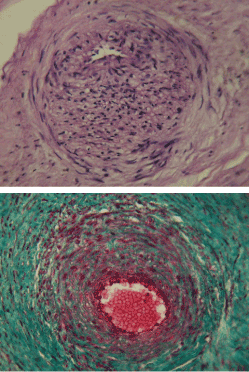
a - internal oblique-longitudinal and outer circular layer of smooth myocytes in the middle shell; b - intertwining bundles of collagen fibers surrounding the artery.
Staining with hematoxylin and eosin (a); by Masson (b). Increase 200.
The index of Ki67 immunopositively nuclei in the blood vessels of the IV and TV chorion of a person with a two-fetal pregnancy is higher than in the case of a single-fetal pregnancy (Table 1). The maximum number of Ki-67 immuno-positive nuclei was detected in the capillary endothelium (2.7 times as compared with the arteries). The level of proliferation of smooth myocytes in the arteries of terminal villi in the case of bifacial pregnancy exceeds by 1.5 times the values of the index for single-fetal pregnancy.
Conduction senders
In the course of the study, it was found that when developing identical twins of a human (at 39-40 weeks of gestation), the villous tree of the monochorionic placenta is represented mainly by TV covered with numerous non-nuclear regions that contact the fetal capillaries and form the syncytiocapillary membranes. This coincides with the morphological picture of the villous tree of the child's place in the X month of single-pregnancy [4,5], where the most numerous species (50%) are also TV. In functional terms, it is important to emphasize that in the zone of fetal sinusoidal capillaries the blood flow slows down and the contact time of the erythrocyte with the placental barrier increases [4]. Therefore, the histological characteristics of placental barriers in single- and two-fetal pregnancies do not have significant structural differences. Analysis of monochorionic placenta of monozygotic twins showed pronounced proliferative activity of trophoblastic epithelium TV. At the end of a single-pregnancy pregnancy, the proliferation marker gives a negative reaction in the epithelium of all types of villi, except terminal ones, where the proliferation index is only 0.5% [5]. It is emphasized that in the peripheral cytotrophoblast cells in the dynamics of pregnancy, the synthesis of DNA is not accompanied by entry into mitosis, but endomitotic reproduction occurs, the cells become polyploid and acquire the ability to migrate [6]. Thus, the registered level of proliferative activity of the epithelium of TV; evidently indicates the incomplete histogenesis of the monochorionic placenta and the growth of the branches of the villous tree in accordance with the functional demands of the two fruits. Relative "immaturity" of the placental barrier can be one of the factors that initiate the development of fetal and placental abnormalities in multiple pregnancies [1,3].
In this work, a significant number of syncytial kidneys on the surface of TV and IV with mononuclear twins is shown. The proliferation index of Ki-67 in the joint of the chorionic twin plate exceeds the values for single-fetal pregnancy. The formation of SK leads to an increase in the total area of villi 1.8 times [5]. The reaction to the Ki-67 marker in the SK epithelium is negative [5], which does not coincide with our results and data on its presence [7].
It is known that joint ventricles, or resorptive nodules, are syncytiotrophoblast (ST) derivatives, are represented by a cluster of ST nuclei [8], the amount of SK increases toward the termination of pregnancy [9]. There is no common opinion on the role of the SK. Some authors consider them to be a product of ST degradation in response to hypoxia [10] or ischemia [11]. The amount of SK can increase with preeclampsia [12]. The joint venture may participate in the emergence of new villi or be able to unscrew, forming free multinuclear symplasts in the intervorsing space, and being carried by blood, revealing itself in remote organs [8]. Probably, free symplasts reflect the consistency of quantitative relationships between the cyto- and syncytiotrophoblast [13]; or are regulators of hemostasis, and, as migrants in the lung parenchyma of the mother, induce immune tolerance to the fetus [5,14].
It was found that the majority of arterial vessels of the placenta chorionic membrane in single and especially multiple pregnancies have in the tunica media expressed oblique-longitudinal and circular layers of smooth myocytes, as well as a well-developed network of elastic fibers. In the arterial basin of the fetus and children's place, we have previously shown the presence in the vascular wall of the complex of additional smooth muscle structures [15], providing normal organo- and histogenesis and creating conditions for optimal distribution of blood flow in the placenta, minimizing trophic and oxygen starvation of the fetus. Vessels of twins in the common placenta are reported with the help of numerous anastomoses [3]. In the field of anastomoses, multiple bends and branches of blood vessels, arteries are able to actively contract and compensate for the limited possibilities of cardiac output in conditions of volumetric loading and increase in blood pressure [4].
Proliferation of the main cellular populations of fetal arteries and capillaries, registered in the course of this work, confirms the observations [5], indicating the vascularization of villi in the third trimester of pregnancy by the mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Thus, the data obtained in the study allow us to conclude that the villous tree of the monochorionic placenta of identical twins in the late neural period of early human development is characterized by incomplete histogenesis of the basic structural components of terminal villi.
References
- Hubinont C, Lewi L, Bernard P, Marbaix E, Debiève F, et al. (2015) Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord in twin gestations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 213: S91-91S102. [Crossref]
- Gaziano EP, De Lia JE, Kuhlmann RS (2000) Diamnionic monochorionic twin gestations: an overview. J Matern Fetal Med 9: 89-96. [Crossref]
- Quarello E, Ville Y (2006) [Specific aspects of monochorionic pregnancies]. Rev Prat 56: 2239-2247. [Crossref]
- Milovanov AP, Savel'yev SV Ed, (2006) Vnutriutrobnoye razvitiye cheloveka. Moscow: MDV.
- Milovanov AP, Yerofeyeva LM, Aleksandrovich NV, Zolotukhina IA (2012) Morfologiya platsenty cheloveka vo II i III trimestrakh beremennosti. Morfologiya 142: 64-67.
- Danilov RK, Borovaya TG (2011) Kratkiy ocherk embriologii cheloveka. V: RK Danilov Ed. 2011. Rukovodstvo po gistologii. 2-ye izdaniye, ispravl. i dopoln. T.2. SPb: SpetsLit, s. 443-509.
- Okamoto T, Seo H, Mano H, Furuhashi M, Goto S, et al. (1990) Expression of human placenta alkaline phosphatase in placenta during pregnancy. Placenta 11: 319-327. [Crossref]
- Novikov VD i Pravotorov GV. 2003. Gistologiya, tsitologiya, embriologiya. Spravochnik. Moscow: OOO Izd-vo YUKEA.
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
- Jain K, Kavi V, Raghuveer CV, Sinha R (2007) Placental pathology in pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) with or without intrauterine growth retardation. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 50: 533-537. [Crossref]
- Devisme L, Merlot B, Ego A, Houfflin-Debarge V, Deruelle P, et al. (2013) A case-control study of placental lesions associated with pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 120: 165-168. [Crossref]
- Burton GJ, Jones CJ (2009) Syncytial knots, sprouts, apoptosis, and trophoblast deportation from the human placenta. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 48: 28-37. [Crossref]
- Rajakumar A, Cerdeira AS, Rana S, Zsengeller Z, Edmunds L, et al. (2012) Transcriptionally active syncytial aggregates in the maternal circulation may contribute to circulating soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 in preeclampsia. Hypertension 59: 56-64. [Crossref]
- Ng YH, Zhu H, Leung PC (2011) Twist regulates cadherin-mediated differentiation and fusion of human trophoblastic cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96: 3881-3890. [Crossref]
- Chamley LW, Chen Q, Ding J, Stone PR, Abumaree M (2011) Trophoblast deportation: just a waste disposal system or antigen sharing? J Reprod Immunol 88: 99-105. [Crossref]
- Gansburgskiy AN, Yal'tsev AV (2015) Osobennosti morfogeneza krovenosnykh sosudov ploda pri platsentarnoy nedostatochnosti beremennykh. Rossiyskiy vestnik perinatologii pediatrii 60: 45-49.


