Cyst hydatid is an infestation caused by the cestodes Echinococcus granulosus. Although pulmonary involvement of hydatid cysts is common in pediatric cases, traumatic pulmonary cyst rupture is rare. In this case report, a 13-year-old male patient with traumatic pulmonary cyst hydatic rupture is presented.
cyst hydatid, ınfestation, pulmonary cyst hydatid rupture, trauma
Hydatid cyst can be placed in all organs and tissues. Lung involvement is the most common after the liver. Hemoptysis, cough, fever, dyspnea and allergic reactions may occur depending on the size and location of the cyst [1]. Pulmonary hydatid cyst is more common in pediatric age group [2]. In this case report, we aimed to draw attention to hydatid cyst rupture in differential diagnosis in patients presenting with clinical findings such as posttraumatic respiratory distress and low saturation in pediatric patients.
In this case we present a patient who was admitted to the Emergency Department of Kafkas University Hospital by 112 ambulance team with dyspnea after falling from the same level. A 13-year-old male fell to his back at the same level. The patient was brought to our emergency department by 112 ambulance team with shortness of breath. Physical examination; conscious, oriental, cooperative, GCS:15, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg, pulse: 144 per/m, oxygen saturation 82%, body temperature 37.8 0C and decreased right lung sounds. Computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a right-sided lung cyst hydatid rupture (Figure 1). pediatric surgery consultation requested. The patient was referred to the Thoracic Surgery Department of Atatürk University because of the need for postoperative pediatric intensive care. He was discharged after the operation with full recovery.
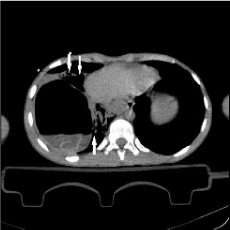
Figure 1. The arrows in the figure indicate ruptures due to hydatid cyst in the right lung
Hydatid cyst is a common parasitic disease in the Kars region, where agriculture and animal husbandry are a source of livelihood in Turkey (3). Our case provided livelihood with livestock. Studies have shown that childhood hydatid cysts are more common in male patients [3,4]. Hydatid cysts are most commonly associated with liver involvement and lung involvement is more common in children. Our case was a 13-year-old male with hydatid cyst of the lung, which was consistent with the literature [3,4]. In a study by Topçu et al. Found that 52.7% of lung hydatid cysts had right lung involvement. Our case was also found to be right lung middle lobe involvement in accordance with the literature [5] . In the study of Tatar et al. 70.5% of pediatric hydatid cyst cases were diagnosed as perforated [6]. In our case, the patient presented to our emergency department with shortness of breath, low back pain and low oxygen saturation after trauma with a ruptured hydatid cyst revealed in CT scan.
Hydatid cyst is a public health problem that does not lose its importance in Turkey. We can reduce the incidence of diesase by educating the public about animal nutrition and slaughter, which is directly related to hygiene conditions. Hydatid cyst is an important disease that should be kept in mind in the differential diagnosis of pediatric emergency department in cases with suspicious clinical and radiological findings in the pediatric disease group.
Source(s) of support in the form of grants, equipment, drugs or all of these
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Declaration on competing interests
None.
Status of ethical clearance for the study along with name of Ethics Committee clearing the research study, and the date and number of the clearance from the committee
Since this is a single case-based observational study, informed consent of the patient is essential and no ethical statement is required.
For the publication of this manuscript, the authors received signed informed consent from the legal guardian of the patient.
- Sarkar M, Pathania R, Jhobta A, Thakur BR, Chopra R. (2016) Cystic pulmonary hydatidosis. Lung India: official organ of Indian Chest Society 33(2): 179. [Crossref]
- Onen A, Şanlı A, Avcı BY (2004) Giant hydatid cyst of the lung: presentation of 10 cases. Toraks Dergisi 5(2): 106-109.
- Karaman Ü, Miman Ö, Kara M, Gıcık Y, Aycan ÖM, Atambay M (2005) Hydatid cyst prevalence in the region of kars. Türkiye Parazitol Derg 29(4): 238-240.
- Hijjawi NS, Al-Radaideh AM, Rababah EM, Al-Qaoud KM, Bani-Hani KE (2018) Cystic echinococcosis in Jordan: A review of causative species, previous studies, serological and radiological diagnosis. Acta tropica 179: 10-16. [Crossref]
- Usluer O, Ceylan KC, Kaya S, Sevinc S, Gursoy S (2010) Surgical management of pulmonary hydatid cysts: is size an important prognostic indicator? Texas Heart Institute Journal 37(4): 429. [Crossref]
- Menekşe G, Özsoy KM, Dağlıoğlu E, Güzel E, Güzel A, Belen D (2012) Pediatric giant-sized ıntracerebral hydatid cyst: Reports of two cases. Journal of Neurological Sciences 29(4).

