A 77-year-old woman was diagnosed as gastric Burkitt lymphoma. At that time, she complained headache and brain computer tomography revealed that she had subdural effusion. Cytology revealed that it was a metastasis of Burkitt lymphoma. Although we started chemotherapy, the patient deteriorated and she passed away.
Subdural effusion by metastatic malignant tumor is very rare. Here we report a first case of subdural effusion in a patient of Burkitt lymphoma and review of the literature.
subdural effusion, Burkitt lymphoma
Subdural effusion occurs by several pathogenesis such as head injury, meningitis and post brain surgical procedures, and so on [1-3]. However, subdural effusion by metastatic malignant tumors is very rare [4]. The common malignant tumors associated with subdural effusion are breast cancer and stomach cancer [5-6]. In hematological malignancies, it is also rare [8-12] and many of the cases were related to intrathecal chemotherapy treatment [13,14]. Here we report a first case of subdural effusion occurred by Burkitt lymphoma and review of the literature.
A 77-year-old woman had tarry stool and she was admitted to a local hospital. Upper gastrointestinal scope was performed and she was diagnosed with gastric Burkitt lymphoma. At that time, she complained headache and brain computer tomography (CT) revealed a crescent-like hypodense subdural effusion in the right parietal region. She did not have previous head injury, anti-coagulant use or thrombocytopenia. Furthermore, the Burkitt lymphoma did not appear in peripheral blood. For further treatment, the patient was transferred to our hospital. On admission, the patient’s left arm showed paralysis and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed the subdural effusion with a midline shift to the left (Figure 1). The low signal of the collected fluid in T1-weighted and high signal in T2-weighted images indicated that the fluid was effusion rather than hematoma. Burr-hole irrigation was performed with a slight bloody fluid. Cytology of the evacuated fluid revealed that the atypical lymphocytes were invaded (Figure 2). The phenotype of the cells were CD10+. CD19+, CD20+ and they showed light chain restriction of lambda chain. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement was positive. Then the patient was diagnosed with a metastasis of Burkitt lymphoma in the brain. Bone marrow biopsy was performed and lymphoma cells were infiltrated in bone marrow. Although we started chemotherapy by R-MPV (rituximab, methotrexate, procarbazine, vincristine), the patient deteriorated rapidly and she passed away.
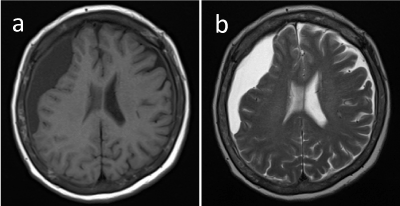
Figure 1. T1-weighted (a) and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the brain. They revealed subdural effusion on the right side.
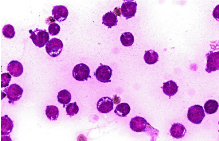
Figure 2. Cytology of the subdural effusion. Lymphoma cells were existed in the collected liquid.
Subdural effusion occurs usually by head injury, meningitis, post brain surgical complication and so on [1-3]. One of the mechanism of pathology is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulation in the inner dural layers of the cerebral convexities from CSF leak, but precise mechanism is unknown yet. Subdural effusion by metastatic malignant tumor is very rare. There are few such cases reported. The common malignancies associated with dural metastasis are breast cancer and stomach cancer [5-7]. In hematological malignancies, only few cases have been reported [8-12] and these were Hodgkin’s lymphoma [8], MALT lymphoma [10], pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia [11] and so on. However, as far as we know, this is the first report that subdural suffusion occurred by Burkitt lymphoma. Some of the cases were related to intrathecal methotrexate chemotherapy [13, 14]. The mechanism of it seems to a reduction in CSF pressure by a lumbar CSF leak and results in downward displacement of the brain with CSF accumulation in the inner dural layers of the cerebral convexities.
It should be remembered that hematological malignancies might be the cause of subdural effusion.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Joy HM, Anscombe AM, Gawne-Cain ML (2007) Blood-stained, acute subdural hygroma mimicking a subacute subdural haematoma in non-accidental head injury. Clin Radiol 62: 703-706. [Crossref]
- Jung TY, Jung S, Jin SG, Jin YH, Kim IY, et al. (2007) Prevention of postoperative subdural fluid collections following transcortical transventricular approach. Surg Neurol 68: 172-176. [Crossref]
- Vinchon M, Joriot S, Jissendi-Tchofo P, Dhellemmes P (2006) Postmeningitis subdural fluid collection in infants: changing pattern and indications for surgery. J Neurosurg 104: 383-387. [Crossref]
- Kamada K, Isu T, Houkin K, Ohsato T, Katoh M, et al. (1991) Acute aggravation of subdural effusion associated with pachymeningitis carcinomatosa: case report. Neurosurgery 29: 464-466. [Crossref]
- Kunii N, Morita A, Yoshikawa G, Kirino T (2005) Subdural hematoma associated with dural metastasis--case report--. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 45: 519-522. [Crossref]
- Mirsadeghi SM, Habibi Z, Meybodi KT, Nejat F, Tabatabai SA (2008) Malignant subdural effusion associated with disseminated adenocarcinoma: a case report. Cases J 18: 328. [Crossref]
- Kimura S, Kotani A, Takimoto T, Yoshino A, Katayama Y (2014) Acute aggravation of subdural fluid collection associated with dural metastasis of malignant neoplasms: case report and review of the literature. Brain Tumor Pathol. 31: 299-303. [Crossref]
- McDonald JV, Burton R (1966) Subdural effusion in Hodgkin's disease. Arch Neurol 15: 649-652. [Crossref]
- Ohtsuki T, Nishimatsu H, Mizukami H, Makishima M, Ohnishi M, et al. (1992) Malignant lymphoma with subdural effusion. Rinsho Ketsueki. 33: 841-843. [Crossref]
- Altundag MK, OziÅŸik Y, Yalcin S, Akyol F, Uner A (2000) Primary low grade B-cell lymphoma of the dura in an immunocompetent patient. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 19: 249-251. [Crossref]
- Kaloostian PE, Chen H, Rupp F, Marchand E (2012) Case of the disappearing subdural hygromas in a pediatric patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 10: 457-458. [Crossref]
- Barrios L, Clément R, Visseaux G, Bord E, Le Gall F (2014) A case of atypical chronic subdural hematoma: a spontaneous rupture of dural lymphoma nodule. J Forensic Leg Med. 22: 145-147. [Crossref]
- Lokireddy P, Dyer MJ (2011) Bilateral subdural hygromas following intrathecal methotrexate. Br J Haematol 155: 536. [Crossref]
- Lewis H, Mahdi AJ, Rowntree C (2015) Bilateral subdural hygromas following administration of intrathecal methotrexate chemotherapy. BMJ Case Rep. [Crossref]
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv


