Abstract
The most characteristic autoimmune encephalopathy syndrome is limbic encephalitis, frequently featuring confusion, memory impairment, psychiatric symptoms and seizures. LGI-1 antibody-associated encephalitis is frequently preceded by a highly characteristic seizure semiology termed faciobrachial dystonic seizure.
Keywords
LGI-1 encephalitis, limbic encephalitis, faciobraquial dystonic seizures
Introduction
Autoimmune encephalopathy syndromes associated with autoantibodies to the voltage-gated potassium channel (VGKC) or its complex proteins were first described in 2001. In 2010, the receptor-associated proteins like contactin-associated protein-like 2 (CASPR2) and leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 (LGI1) were identified as the antigenic targets in most cases of VGKC antibody-associated syndromes [1-3].
Autoantibodies against the extracellular domains of the VGKC complex protein, LGI1,and CASPR2 have been described in patients with limbic encephalitis (LE), neuromyotonia, and Morvan syndrome. In patients suffering from LE, LGI1 is the most commonly targeted VGKC-complex protein. It has been shown that identifying LGI 1 antibody has a better sensitivity and specificity than VGKC-complex antibody testing in providing a diagnosis and rationale immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases. Amnesia, confusion, and seizure are the main symptoms of LGI1-related LE. Recently, another distinctive symptom involving brief, very frequent episodes that typically involve dystonic posturing of the hemiface and ipsilateral arm (faciobrachial dystonic seizures, FBDS) has been described and is currently viewed as pathognomonic for the presence of LGI1 antibodies[4-6].
Case history
A 43-year old female presented with a 6-month medical history of severe anxiety symptoms which progressed to hallucinations. Antipsychotic medication (risperidone 1mg/day) was administrated to control hallucinations 2 months prior to admission when the patient started presentingsporadic generalized tonic-clonic seizures and cognitive decline (memory impairment and confusion). The patient became worse 1 week prior to admission and was admitted to the emergency service with generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Her Glasgow coma scale score was 7 (E2V1M4), and the seizure persisted. She was intubated and placed on respiratory support. Antiepileptic drugs (1500mg of fosphenytoin and 20mg of diazepam) were administrated and midazolam was continued after intubation. Her neurologic examination was unremarkable except for her reduced level of consciousness. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the head didn´t show abnormalities. Her complete blood count and electrolytes revealed hyponatremia (120mmol/L).A lumbar puncture was performed and thecerebrospinal fluid analysis (proteins, glucose, red and white blood cells, bacteria) were normal. The patient was submitted to thoracic, abdominal and pelvic CT scans which were unremarkable. Infectious tests (HIV, HCV, HBC, VDRL, HSV-1,HSV-2, VZV, CMV),rheumatologic disease studies (RF,ANA, complement test, c-ANCA, p-ANCA), and tumor markers (CEA,CA 19-9, anti-TPO) were normal. The patient was extubated after generalized tonic-clonic seizures ceased but continued to present confusional state and several episodes of dystonic posturing of the face and right arm (Figure 1-2). Magnetic resonance imaging documented bilateral hippocampal high intensity signal on T2/Flair weighted images(Figure 3).EEG recording revealed disorganized slow activities with preserved reactivity. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid was sent to KlinischesInstitutfürNeurologie in Wien to analyze the presence of anti-neuronal antibodies. Screening on a tissue-based assay for surface receptor antibodies (avidin-biotin-peroxidase technique;rat brain) showed a specific neuropil staining and a subsequent performed cell-based assay (IIFT; Euroimmun) was positive for anti-LGI1 antibodies with the antibody titer in serum of 1:12800 (primary dilution 1:200) and the antibody titer in CSF of 1:256 (primary dilution 1:2). A tissue-based assay (avidin-biotin-peroxidase technique; rat-cerebellum) for onconeuronal antibodies (Hu, Yo, Ri, Tr, CV2, amphiphysin, Ma1/2), PKCgamma, CARPVIII, ARHGAP26, tumor-associated antibodies (SOX1, ZIC4) and non-tumor-associated antibodies (GAD65, AK5, Homer3) was negative. The patient was treated with immunotherapy. First, she received intravenous methylprednisolone pulsotherapy (1g/d for 5 days) without significant improvement. After the first pulsotherapy, she received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG- 0,4g/Kg/d for 5 days), had a partial improvement and was discharged with reduced seizure episodes, more awake but with significant cognitive impairment. After 1 month she was readmitted to the hospital because she was very somnolent and the frequency of faciobraquial dystonic seizures had increased. She received intravenous cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m2/day, and more alert with fewer FBDS, was discharged to outpatient follow-up.
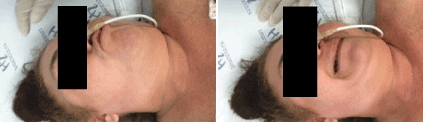
Figure1. Dystonic face movements
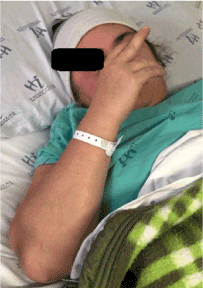
Figure 2. Dystonic arm movement
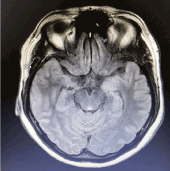
Figure3.Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrating bilateral hippocampal high intensity signal on T2/Flair weighted images
References
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
- 1.Pollak TA, Moran N (2017) Emergence of new-onset psychotic disorder following recovery from LGI1 antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. BMJ case reports10.1136/bcr-2016-218328.
- 2.Buckley C, Oger J, Clover L, Tuzun E, Carpenter K, et al. (2001) Potassium channel antibodies in two patients with reversible limbic encephalitis. Annals of neurology50:73-8. [Crossref]
- 3.Irani SR, Alexander S, Waters P, Kleopa KA, Pettingill P, et al. (2010) Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan's syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia. Brain: a journal of neurology133:2734-2748[Crossref]
- 4.Chen C, Wang X, Zhang C, Cui T, Shi WX, et al. (2017) Seizure semiology in leucine-rich glioma-inactivated protein 1 antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. Epilepsy &behavior77:90-95[Crossref]
- 5.Vincent A, Buckley C, Schott JM, Baker I, Dewar BK, et al. (2004) Potassium channel antibody-associated encephalopathy: a potentially immunotherapy-responsive form of limbic encephalitis. Brain: a journal of neurology127:701-12[Crossref]
- 6.Irani SR, Michell AW, Lang B, Pettingill P, Waters P, et al. (2011)Faciobrachial dystonic seizures precede Lgi1 antibody limbic encephalitis. Annals of neurology69:892-900.[Crossref]



