Introduction
Depression isn't solely a state of being unhappy; it is an illness that conquers the flexibility to feel emotion, whether or not sensible or unhealthy, whatsoever. It not only involves the mind, it additionally involves the body and thoughts. In several cultures some complain of excessive headaches and extreme pain and this can be known as depression, moderate or otherwise. This illness is passed down through genes or will follow external events or may be caused by a chemical imbalance in the brain. Depression affects common fraction of all Americans, some while not even knowing it, at some time throughout their lives. Depression isn't an illness that solely influences males or youngsters of the age three to eleven [1]. Each individual is at risk of depression. Although women are three times additional seemingly to become depressed than men, men are 5 times additional seemingly to commit suicide when depressed than women [2]. There are differing types of depressions like major depression, persistent depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, seasonal effective disorder, psychotic depression, postpartum depression, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, situational depression, atypical depression [3]. Out of that the foremost severe case being the major depression. For some people major depression may end up in severe impairments that interfere with or limit one's ability to hold out major life activities. Though all age groups are open to depression, teenagers are the most common to be detected of being tormented by the sickness. This is often most likely as a result of peer pressure and also the changes in their life [4]. The aim this study was to understand the impact of clinical depression among the non-institutionalized adolescents and older population.
Causes and symptoms
The exact reason for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) isn't best known. However, there are many factors that may increase the chance of developing the condition. A combination of genes and stress will have an effect on brain chemistry and scale back the power to take care of mood stability. Changes in the balance of hormones would possibly continue to contribute to the event of MDD. This disorder might continuously be triggered by alcohol or substance abuse [5], sure medical conditions, like cancer or glandular disorder, specific sorts of medications including steroids. It may also include physical or mental abuse, conflict, death or loss, major life events, serious illness and other personal and professional problems [6].
The practicing physician or the psychological professional will create an MDD based on diagnosis of symptoms, feelings, and behavior patterns. The practitioner will raise certain queries or will provide with a questionnaire so that they will verify whether or not the individual got MDD [7]. In keeping with its criteria, you want to have five or a lot of the subsequent symptoms and experience them a minimum of once each day for a period of quite a pair of weeks. The symptoms includes: feeling unhappy or irritable most of the day, nearly every day; feeling less fascinated by most activities you once enjoyed; sudden loss or gain weight or have a modification in appetite; trouble falling asleep or wish to sleep over usual; expertise feelings of restlessness; feeling unusually tired and have an absence of energy; feeling unworthy or guilty; issues in concentrating, thinking, or making selections; thinking about harming yourself or committing suicide [8].
Methods
The prevalence information given here for major depressive episodes are from the 2016 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) [9]. The NSDUH study definition of major depressive episode is predicated primarily on the fourth edition of the Diagnostic and applied math Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV):
- An amount of fortnight or longer throughout which there's either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure, and a minimum of four alternative symptoms that replicate a modification in functioning, like issues with sleep, eating, energy, concentration, self-image or repeated thoughts of death or suicide.
- For the NSDUH survey - in contrast to DSM-IV criteria - no exclusions were created for a serious depressive episode caused by medical sickness, sadness, or substance use disorders.
- Modules associated with major depressive episode derived from DSM-IV (1994) criteria for major depression were enclosed within the NSDUH questionnaire. The queries were custom-made from the depression module within the National Co-morbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). Revisions to the queries within the modules were created primarily to cut back their length and to change the NCS-R queries that are interviewer-administered to the Audio Computer-Assisted Self-Interviewing (ACASI) format utilized in NSDUH. Additionally, some revisions, supported cognitive testing, were created to enhance comprehension. Moreover, although titles like those utilized in the NCS-R were used for the NSDUH modules, the results of those things might not be directly comparable. This is primarily because of differing modes of administration in every survey (ACASI in NSDUH vs. computer-assisted personal interviewing in NCS-R), revisions to phrasing necessary to take care of the logical processes of the ACASI surroundings, and potential context effects ensuing from deleting queries not expressly pertinent to major depression
- The Sheehan disability Scale (SDS) was accustomed assess the impact of major depressive episode on a person’s life. The SDS is a brief self-report tool with ratings from zero to ten (with ten being the highest) for the extent of impairment caused by the disorder in each of 4 role domains: home management, work, close relationships with others, and social life. A rating of ≥ 7 in a minimum of one domain is taken into account to be severe impairment. Respondents were excluded if SDS role impairment severity was unknown, or if specific activities listed within the SDS weren't applicable.
Population
The totality of NSDUH respondents for the major depressive episode estimates is that the civilian, non-institutionalized population aged 12-17 (adolescents) and 18 years old or older (adults) residing within the US. The survey covers residents of households, and persons in non-institutional cluster quarters (e.g., rooming/boarding homes, school dormitories, and migratory workers' camps). This survey doesn't include persons who, for the whole year, had no permanent address (e.g., homeless and/or travellers), who were on active military duty; or who resided in institutional cluster quarters (e.g., punitive facilities, nursing homes, mental institutions, long-run hospitals).
Results
Prevalence of major depressive episode among adolescents
A calculable 3.1 million adolescents within the US had a minimum of one major depressive episode. This number depicted 12.8% of the US adolescents. The prevalence of major depressive episode was higher among adolescent females (19.4%) compared to males (6.4%). The prevalence of major depressive episode was highest among adolescents reported 2 or additional races (13.8%) (Figure 1).
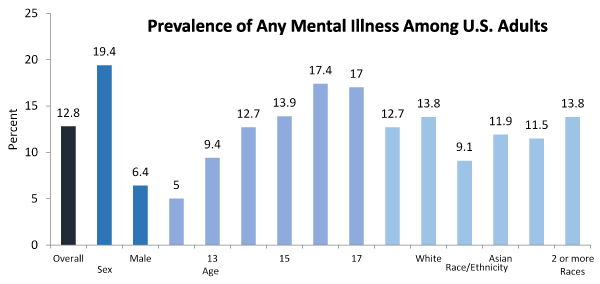
Figure 1. Prevalence of major depressive episode among U.S. adolescents in 2016
Treatment of major depressive episode among adolescents
Treatment varieties enclosed caregiver only, medication only, and combined caregiver and medicine. A calculable nineteen received care by a caregiver alone and another nineteen received combined care by a caregiver and medicine treatment. Treatment with medication alone was least common (2%). Approximately hour of adolescents with major depressive episode didn't receive treatment (Figure 2).
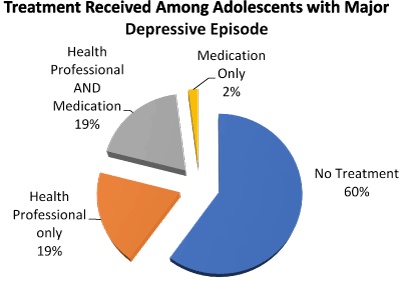
Figure 2. Treatment received among the past year by U.S. adolescents aged 12-17 with major depressive episode in 2016
Treatment
Major or Clinical Depression is a serious however treatable health problem. Depending on the severity of symptoms, your medical aid doctor or a specialist could suggest treatment. A large range of treatments are available for depression and new treatments (particularly medications) often appear. Continuing research implies that the proof for how well a treatment works is usually ever-changing too. Depressions that are a lot of biological in their origins of melancholic depression and psychotic depression has more probability to wish physical treatments like antidepressants and less probability to be resolved with psychological treatments alone. Non-melancholic depression that is linked to psychological factors, temperament characteristics and disagreeable life events, responds to each psychological treatments and physical treatments. May also recommend psychotherapy, or talk therapy, during which you address your emotional state.
Conclusion
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
Depression’s price to the US economy each year is estimated at 44 billion greenbacks [10]. This sickness is second only to cancer on the impact of our society. By itself depression will cause extreme disappointment, anxiety, insomnia and even thoughts of suicide. And yet, we don’t have an enormous organization to assist those that suffer from it. There's no “Association for Depressed.” Why is this? Why don’t the people of the US place one thing together to support and guide those that are suffering from depression?
Depression isn't a matter to take thinly. It's not one thing to head off frequently, however to take to heart and realize help. Many individuals commit suicide on a daily basis due to depression. If you're or grasp somebody who is depressed get help. Don't hold it in forever, for you may be prone to the same issue. Lots of individuals get depression confused with extreme unhappiness. Depression isn't a term simply to be thrown around; it's a severe state of being.
References
- Schmidt CW (2007) Environmental connections: a deeper look into mental illness. Environ Health Perspect 115: A404-A410. [Crossref]
- Albert PR (2015) Why is depression more prevalent in women? J Psychiatry Neurosci 40: 219-221. [Crossref]
- Benazzi F (2006) Various forms of depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 8: 151-161. [Crossref]
- Gayman MD, Turner RJ, Cui M (2008) Physical limitations and depressive symptoms: exploring the nature of the association. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 63: S219-S28. [Crossref]
- Brook DW, Brook JS, Zhang C, Cohen P, Whiteman M (2002) Drug use and the risk of major depressive disorder, alcohol dependence, and substance use disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59: 1039-1044. [Crossref]
- Paterniti S, Sterner I, Caldwell C, Bisserbe JC (2017) Childhood neglect predicts the course of major depression in a tertiary care sample: a follow-up study. BMC Psychiatry 17: 113. [Crossref]
- Kennedy SH (2008) Core symptoms of major depressive disorder: relevance to diagnosis and treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 10: 271-277. [Crossref]
- Perlman K, Benrimoh D, Israel S, Rollins C, Brown E, et al. (2018) A systematic meta-review of predictors of antidepressant treatment outcome in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 243: 503-515. [Crossref]
- Park-Lee E, Lipari RN, Hedden SL, Kroutil LA, Porter JD (2016) Receipt of Services for Substance Use and Mental Health Issues Among Adults. CBHSQ Data Review, Rockville (MD). [Crossref]
- Chiu M, Lebenbaum M, Cheng J, de Oliveira C, Kurdyak P (2017) The direct healthcare costs associated with psychological distress and major depression: A population-based cohort study in Ontario, Canada. PloS one 12: e0184268. [Crossref]


