Areca catechu L. is a palm plant, widely distributed in the tropical and subtropical districts, such as southeast Asia and Hainan, Taiwan, Hunan and Fujian in China. Some studies on the chemical components (alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, triterpenes, fatty acids, etc.) and biological activities (anti-bacterial, anti-viral and anti-tumor, anti-oxidation, anthelmintic action, effects on the nervous system and effects on the digestive system) have been reported. This review briefly describes the research progress of the chemical components and biological activities of Areca catechu L, to provide the reference to the researchers.
Areca catechu L., chemical components, biological activities
Areca catechu L. is a palm family areca plants, perennial evergreen trees and is widely cultivated in tropical areas. In south of China, it is also widely distributed in Taiwan, Hunan, Guangdong, Hainan and Fujian. China is one of the world’s major producers of areca nut. The main chemical constituents of areca have been identified as: alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, triterpenes, fatty acids, etc., which also possess a wide spectrum of biological activities, such as Anti-bacterial, anti-viral and anti-tumor, anti-oxidation, anthelmintic action, effects on the nervous system and digestive system. This review describes the previous research on bioactive compounds of Areca catechu L. and biological activities of both the extracts and isolated compounds from this medicinal plant.
Shen reported that the main components of the fruits of Areca catechu L. are phenols (31.1%), polysaccharides (18.7%), fat (14.0%), fiber (10.8%) and alkaloids (0.5%). While the main ingredients of its flower are alkaloids and polyphenols [1]. The components were classified and described as below
Polyphenols
The polyphenols in the fruits of Areca catechu L. are phenolic acids, flavonoids and xylophenolic acids. They are mainly present in the roots, stems, leaves and fruits of Areca catechu L., and the amounts of them are related to the growth cycle and maturity.
Lin et al. obtained the total phenol from the flowers of Areca catechu L. through the boiling water extract method. The contents of the total phenol and flavonoids were 406.43 g/mL and 840.73 g/mL respectively. The authors also extracted the contents of total phenol and flavonoids using water/methanol and determined their contents, which were 451.47 g/mL 880.00 g/mL respectively [2]. Zhang obtained the total phenol from the three different flowers of Areca catechu L. and determined its contents to be: 0.6236 g/mL, 0.5893 g/mL, 0.3146 g/mL [3]. The extractions of three flowers contain the same compounds, such as gallic acid, coumaric acid, epicatechin, ferulic acid, rutin and naringin. While the contents of epicatechin (1), gallic acid (2) and coumaric acid (3) are relatively higher than others (Figure 1).
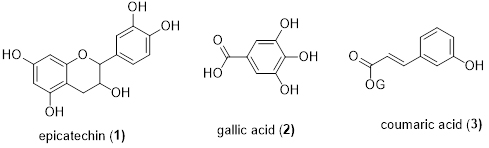
Figure 1. Respective structures of phenols
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are mainly contained in the seed and fruit of Areca catechu L.. Zhang et al. obtained four flavonoids from the fruits of Areca catechu L.: isorhamnetin (4), chrysoeriol (5), luteolin (6) and (±)- 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-7-methoxychroman-4-one (7) [4]. Yang et al. obtained quercetin (8), (s)-5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-7-methoxychroman-4-one (9) and Liquiritigenin (10) from its seed (Figure 2) [5].
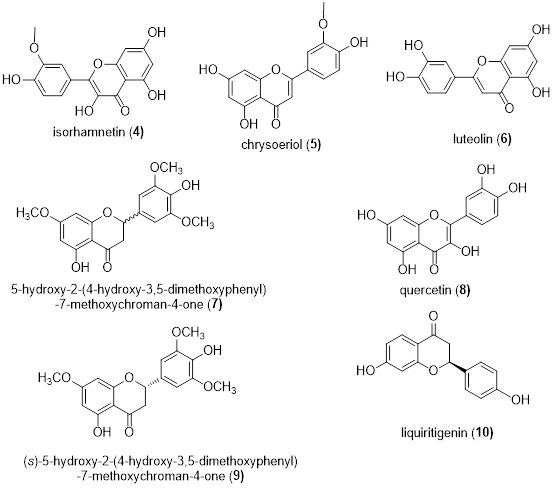
Figure 2. Flavonoids obtained from the seed and fruit of Areca catechu L.
Tannins
The tannins in Areca catechu L. are tannins (proanthocyanidins), also named as flavanol derivatives, which exist after combining with arecoline and the content in Areca catechu L. is about 15%. Some tannins have been isolated and confirmed as arecatannin A1, arecatannin A2, arecatannin A3, arecatannin B1, arecatannin B2 arecatannin C1 [6,7].
Triterpenes and steroids
Saeed et al. isolated ursolic acid (11), ursolic acid acetate (12) and sitosterol (13) from the leaves of Areca catechu L. [8], and isolated arborinol (14), cylindrin (15), fernenol (16) and arundoin (17) from the peel [9]. Yang et al. isolated cycloatanol (18), ergosterol peroxide (19) and B-sitostenone (20) from its seeds (Figure 3) [5].
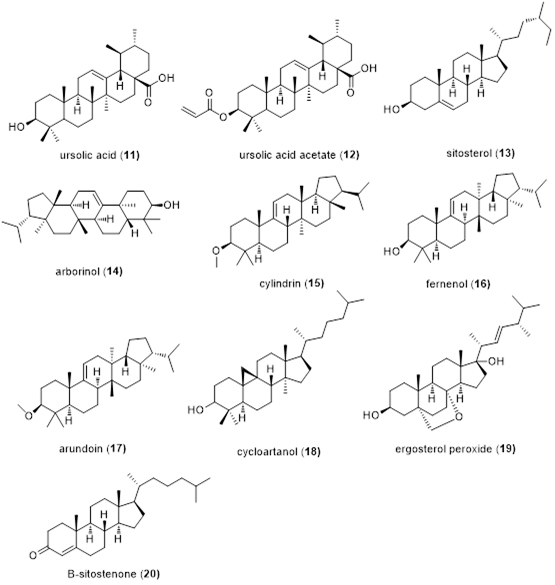
Figure 3. Triterpenes and steroids obtained from Areca catechu L.
Fatty acids
The fatty acids were mainly contained in the seeds of Areca catechu L., and the total content of fatty acid is about 14%. The lauric acid (21), myristic acid (22), palmitic acid (23), stearic acid (24), oleic acid (25), linoleic acid (26), α-lipoic acid (27), decanoic acid (28), decanoic acid (29) and seventeen carbonate (30) have been identified (Figure 4) [10].
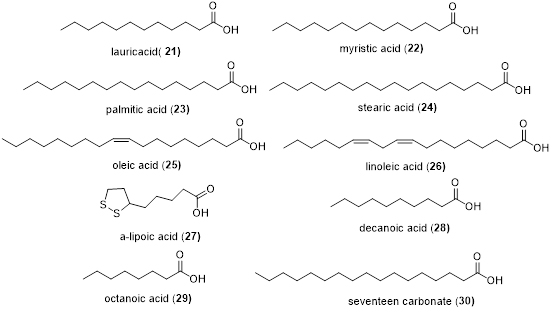
Figure 4. Fatty acid obtained from the seeds of Areca catechu L.
Zhou et al. identified 11 kinds of fatty acids and their contents by GC-MS, among which the contents of linoleic acid (26), oleic acid (25) and palmitic acid (23) were higher than others and with 32.12%, 29.50% and 27.70%, respectively (Figure 4) [11]. Guo et al. extracted the fruits of Areca catechu L. using petroleum ether and also identified the fatty acids and their contents by GC-MS. The results are listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Chemical components of fatty acid in fruits of Areca catechu L.
|
Compounds
|
Molecular formula
|
Formula weight
|
Relative amount (%)
|
|
Arecoline
|
C8H13NO2
|
155
|
7.00
|
|
2,6-Di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol
|
C15H25O
|
220
|
5.51
|
|
Methyl cinnamate
|
C10H10O2
|
162
|
0.68
|
|
Nonanoic acid
|
C9H18O2
|
158
|
0.54
|
|
2,4-Di-t-butylphenol
|
C14H22O
|
206
|
6.54
|
|
Benzoic acid
|
C7H6O2
|
122
|
0.75
|
|
Lauric acid
|
C12H24O2
|
200
|
5.76
|
|
Myristic acid
|
C14H28O2
|
228
|
13.33
|
|
Pentadecanoic acid
|
C15H30O2
|
242
|
1.05
|
|
Palmitic acid
|
C16H32O2
|
256
|
25.53
|
|
Stearic acid
|
C18H36O2
|
284
|
5.89
|
|
Oleic acid
|
C18H34O2
|
282
|
16.01
|
|
Linoleic acid
|
C18H32O2
|
280
|
7.67
|
Amino acids
It is reported that the content of proline (31) and tyrosine (32) in Areca catechu L. was over 15% and 10% respectively. The phenylalanine (33), arginine (34), a small amount of tryptophan (35) and methionine (36) were also confirmed in Areca catechu L.. Mou et al. isolated N-benzoylphenylalanylphenylalinol acetate (37) and TMS-58B (38) from Areca catechu L. [12]. You et al. reported that there are at least 17 amino acids in Areca catechu L., among which the contents of aspartic acid (39), glutamic acid (40), lysine (41) and arginine (34) were higher than other amino acids (Figure 5) [13].
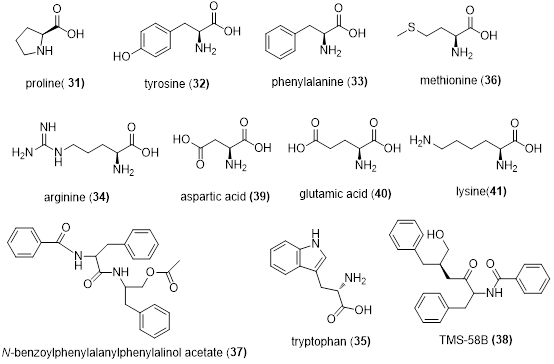
Figure 5. Amino acids confirmed from Areca catechu L.
Alkaloids
Areca catechu L. is only one containing alkaloids among 54 kinds of palm species, and there are much difference of the alkaloids in different organs and tissues of Areca catechu L.. The total alkaloids in Areca catechu L. is 0.3-0.6%, which are mainly arecoline (42), arecaine (43), guvacoline (44), guvacine (45), arecolidine (46), homoarecoline (47) and isoguvacine (48) (Figure 6) [14-16].
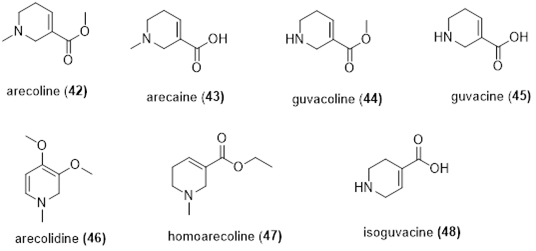
Figure 6. Alkaloids isolated from Areca catechu L.
Anthelmintic activity
As a Chinese traditional plant medicine, Areca catechu L. has been widely used as an anthelmintic agent because it can inhibit or kill a variety of parasites. Arecoline is the active ingredient, which can help flush the pig tapeworm, the crow tapeworm, the man type bloodsucking worm, the liver fluke and the worm out the host body by paralyzing the nervous system of the pig tapeworm, the crow tapeworm, the man type bloodsucking worm, the liver fluke and the worm. In addition, arecoline can also increase the ability of pentachlorophenol sodium against oncomelania.
Effects on the nervous system
Arecoline can stimulate muscarinic receptor and promote the body excitability. Arecaine and gubacine can bind with brain GABA receptor, and prevent the ability of GABA on nerve transmission, thus make people feel happy.
Arecoline can relieve drunk state. In addition, it can also improve the cognitive function and memory of patients with Alzheimer's disease. In 2000, a study showed that the total alkaloids of Areca catechu L., especially arecoline could relieve the patient's mood of schizophrenia and depression.
Effects on the digestive system
“Areca Sixiao Wan”, included in the 2015 edition of the Chinese pharmacopoeia, is used to treat indigestion, bloating and constipation. Arecoline is a kind of muscarinic receptor agonist, it can stimulate choline muscarinic receptor, and make the gastrointestinal smooth muscle tension increased, promote digestion by making gastrointestinal smooth muscle tension increased, increasing gastrointestinal peristalsis and enhancing saliva secretion. Zou et al. found that areca had significant contractile effect on gastric smooth muscle of functional dyspepsia model rats by enhancing contractile amplitude [17,18].
Effects on the endocrine system
The effect of arecoline on the endocrine system is mainly to increase the release of endogenous corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) by stimulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortical axis and block the flow of calcium ions into the adrenal medulla pheochromocyte. Dasgupta et al. also reported that arecoline can stimulate and inhibit adrenal activity and inhibit adrenal hormone in mice to produce immune effect [19].
Effects on cardiovascular lipids
At present, areca is included in some medicines for reducing blood pressure and blood lipids. Ling et al. reported that arecoline can improve ACh-induced vasorelaxation in high fructose-fed rats, and the potential mechanism might be associated with the increasing of cystathionine-c-lyase expression and activation of KATP channels [20]. Duan and Wang reported that arecoline has regulation effects on D-glucose induced excess mRNA expression of ICAM-1, MCP-1 and vascular cell adhesive molecule-1 (VCAM-1) [21].
Oxidation resistance
It is reported that Areca catechu L. has strong antioxidant ability, which is mainly due to the polyphenols and flavonoids. Zhang et al. reported that the ethanol extract of areca seed exhibited stronger scavenging ability on DPPH free radical, hydroxyl free radical and superoxide anion free radical than that of dibutyl hydroxyl plus toluene [22]. It was also reported that the extraction of areca exhibited higher antioxidant activity than that of resveratrol.
Anti-bacterial, anti-viral and anti-tumor effects
The alcohol extraction of areca possess antibacterial activity against 38 bacteria, such as E. coli, candida albicans, tropical bacteria and interdactylobium, and has a good inhibitory effect on common bacteria in the mouth, such as streptococcus, porphyria gingivalis and fumigate bacteria, as well as actinomycetes [23,24]. It also reported that areca possess anti-flu virus activity.
In addition, Huang et al. reported that arecoline could prevent BCC tumourigenesis by reducing the levels of the tumour cell survival factor IL-6, increasing levels of the tumour suppressor factor p53, and eliciting cell cycle arrest, followed by apoptosis [25]. Another research suggested that arecoline induced death of Human Leukaemia K562 cells was associated with up-modulation of TNFR2 surface expression [26].
Toxicity and side effects
LARC (international centre for research on cancer) identified betel nut as a primary carcinogen in its special issue no. 85 of 7 August 2003. Chewing betel nut causes submucosal fibrosis, and then cause oral cancer. Arecoline is the main alkaloid that causes the expression of αvβ6, which is regulated by the M4 (muscarinic acetylcholine) receptor, while high expression of αvβ6 is found in 80% of oral cancers caused by submucosal fibrosis [27].
Arecoline, the active ingredient of betel nut, can also affect the reproductive system. Hu et al. reported that water extraction of areca could affect the sperm of male mice, which can reduce the number of sperm, reduce the vigour and increase the deformity rate. Areca nut is toxic to reproductive function of male mice [28]. Arecoline can cause chromosome aberrations in mouse bone marrow cells. Even if, it also increases the exchange frequency of sister chromosomes, make germ cells abnormal morphology, thus make DNA synthesis disorders [29].
This paper reviewed the recent studies on the chemical constituents and biological activities of Areca catechu L.. Through reviewing the progress of the chemical components and biological activities of Areca catechu L., only some simple studies have been carried out. Areca catechu L. is a kind of Chinese Traditional plant medicine, we must develop this plant medicine and focus on identification and quantification the bioactive compounds responsible for each biological activity that Areca catechu L. displays. There should be adequate studies on elucidation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the activity of these bioactive compounds, which can lead to use of this plant medicine for drug development. These years, our research group carried out the isolation of the subtropical plant medicines and their biological evaluation, and we have obtained remarkable results. Areca catechu L. has been planted in Fujian province with large-scale. Our subsequent work will focus on the isolation and biological evaluation of Areca catechu L. planted in Fujian.
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21875252) and Self-created Area Project of Major Science Technology Innovation Platform of Xiamen(3502ZCQ20171002).
- Shen XL, Duan LL (2009) Advances in chemical constituents and pharmacology of areca. J Yichun Coll 31: 95-97.
- Lin ES, Li CC (2010) Evaluation of superoxide radical scavenging capacity and reducing power of areca flower extracts. J Med Plant Res 4: 975-981.
- Zhang CM, Wang YF, Wnang HY, et al. (2011) Determination of 9 polyphenolic compounds including gallic acid in areca flower extract. J Tropical Crops 32: 965-969.
- Zhang X, Mei WL, Zeng YB, et al. (2009) A preliminary study on phenolic chemical constituents and antibacterial activity of areca. Acta Tropical Subtropical Flora 17: 74-76.
- Yang WQ, Wang HC, Wang WJ, Wang Y, Zhang XQ, et al. (2012) Chemical constituents from the fruits of Areca catechu. Zhong Yao Cai 35: 400-403. [Crossref]
- Wang JK, Sun LX (1993) Analysis of phenolics compounds in areca nut chewers. J China Agricultural Chem Soc 31: 623-632.
- Zhang CJ, Lv FJ, Tai JX, et al. (2008) Determination of total phenols and tannins in areca nut and its products. Food Res Dev 29: 119-121.
- Saeed SA, Farnaz S, Simjee RU, Malik A (1993) Triterpenes and β-sitosterol from piper betle: Isolation, antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory effects. Biochem Soc Trans 21: 462S. [Crossref]
- Yenjit P, Issarakraisila M, Intana W, Chantrapromma K (2010) Fungicidal activity of compounds extracted from the pericarp of Areca catechu, against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in vitro, and in mango fruit. Postharv Biol Technol 55: 129-132.
- Yi P, Tang YR, Zhou F, et al. (2019) Advances in chemical consituents and pharmachological activities of betel nut. Chin Herbal Med 50: 2498-2504.
- Zhou WH, Li ZH, Zhang HD, et al. (2010) Extraction and fatty acid analysis of areca nut oil. Chin J Grain Oil 25: 38-41.
- Mou XN, Yang WQ, Wang WJ, et al. (2014) The chemical composition of betel nut. J Jinan University 35: 56-60.
- You ZJ, Yu H, Shi HB (1996) Analysis and study on amino acid composition and content of meat, skin, flower, stem and root of penang nut. Fujian Anal Testing 5: 581-583.
- Chinese Academu of Medical Sciences (1972) Study on active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicine. People’s Medical Publishing House 1: 445.
- Jahns E (1888) Ueber die Alkaloide der Arecanuss. Ber Deut Chem Gesellsch 21: 3404-3409.
- Huang JL, McLeish MJ (1989) High-performance liguid chromatographic determination of the alkaloids in betel nut. J Chromatogr 475: 447-450.
- Sullivan RJ, Allen JS, Otto C, Tiobech J, Nero K (2000) Effects of chewing betel nut (Areca catechu) on the symptoms of people with schizophrenia in Palau, Micronesia. Br J Psychiatry 177: 174-178.
- Zou BC, Wei LF, Wei MX (2003) Effects of betel nut on gastric motility in rats with functional dyspepsia. Chin J Integrational Traditional Chin Western Med Digestion 11: 6-8.
- Dasgupta R, Chatterji U, Nag TC, Chaudhuri-Sengupta S, Nag D, et al. (2010) Ultrastructural and hormonal modulations of the thyroid gland following arecoline treatment in albino mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 319: 1-7. [Crossref]
- Ling HY, Wang G, Zhang W, Li X, Zhou SH, et al. (2012) Arecoline improves vascular endothelial function in high fructose-fed rats via increasing cystathionine-c-lyase expression and activating K(ATP) channels. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33: 1023-1029. [Crossref]
- Duan Z, Wang H (2006) Regulation effect of arecoline on excess expression of adhesive molecules in endothelial cells injuried with high concentration of d-glucose. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther 11: 27–31.
- Zhang L, Zheng YJ, Li Y, et al. (2016) Study on antioxidant activity of areca seed ethanol extract. Food Res Dev 37: 102-104.
- Xiao Y, Liu TJ, Huang ZW, et al. (2001) Effect of natural drugs on the growth and acid production of streptococcus sanguis in vitro. Chin J Microecol 13: 278.
- Huang BB, Fan MW, Yang XL, et al. (2003) Effects of Chinese herbs on the growth of periodontal bacteria. J Fourth Military Med Univ 24: 424.
- Huang LW, Hsieh BS, Cheng HL, Hu YC, Chang WT, et al. (2012) Arecoline decreases interleukin-6 production and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human basal cell carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258: 199. [Crossref]
- Chen YJ, Chang LS (2012) Arecoline-induced death of human leukemia K562 cells is associated with surface up-modulation of TNFR2. J Cell Physiol 227: 2240-2251. [Crossref]
- Moutasim KA, Jenei V, Sapienza K, Marsh D, Weinreb PH, et al. (2011) Betel-derived alkaloid up-regulates keratinocyte alphavbeta 6 integrin expression and promotes oral submucous fibrosis. J Pathol 223: 366. [Crossref]
- Hu YX, Zang XB, Hu YM, et al. (1999) Effects of betel nut on fertility of male mice. Pract Prevent Med 6: 172.
- Luan J, Tao XY (2018) Research progress on biological activity of areca nut. Anhui Agricultural Sci Bull 24: 8-12.






