Abstract
Cases of Diabetes II have been rising in Saudi population. The main objective of our study was to analyze the relationship between the inheritance of ABO blood group and Rh factors and the development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in male population of Hail region of Saudi Arabia. Random community survey of about 200 local educated youth (under 18) and non-college going adults revealed high prevalence of T2DM among adult male population (27.5%) as compared to the educated youth population (5.5%).
In this study we first looked at the distribution of ABO and Rhesus (Rh) blood group antigen data of 490 non diabetic control group (283 females (57.7%) and 207 (42.4%) male and compared it with 342 diabetes type 2 patients (214 females and 128 male) who were admitted to the Diabetic clinic of King Khaled Hospital in Hail Saudi Arabia between 2008 and 2015. Out of 342 patients 214 (62.6%) were females and 128 (37.4 %) were males.
Our results show that out of 207 control non diabetic individuals (males only) 6 were A- (2.89%), 43 were A+ (20.8%), 2 were AB- (0.96%), 9 were AB+ (4.3%), 7 were B- (3.38%), 44 were B+ (21.2%), 7 were O- (3.4%) and 89 were O+ (42.9%). So in control population O+ was the most prevalent blood group (42.9%) and B+ was the second most prevalent blood type (21.2%).
Next we wanted to see if the blood group distribution patterns are similar among T2DM patients. Analysis of our results show that 2.3% of T2DM male patients were A-, 22.65% were A+, 0% were AB-, 4.7% were AB+, 0% were B- but 30.5% were B+ as compared to the 21.2% B+ among control group. Only 0.78% were O- and 39.1% were O+. When we looked at the distribution of Rh antigen in the control population we found 89.4% people to be Rh+ and 10.6% Rh- however among diabetics 96.9% patients were Rh+ and 3.13% were Rh-. These results suggest a 3.4 fold decrease in Rh- individuals among diabetics (3.13% Rh-) as compared to the control population (10.9% Rh-).
So in conclusion percentage of Rh- individuals among T2DM male patients is reduced by 3.4 fold (3.13% Rh-) as compared to the control group (10.6% Rh-). Our results also show that blood group B+ is expressed in much higher percentage in diabetics (30.5%) as compared to the controls (21.2%). Additionally O+ is expressed in 42.9% controls but show a slight yet significant reduction in its distribution (39%) among T2DM patients. These results suggest that B+ offers least resistance to male T2DM patients and O+ provides a slight resistance to diabetes.
Key words
overweight, child obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), blood group (ABO), rhesus antigen (Rh), insulin receptors
Introduction
Obesity is growing very rapidly in many countries around the globe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) bulletin, in 2014, there were more than 1.9 billion overweight adults in the world (WHO 2015 updates). WHO study further adds that in 2014, 39% of the adults (above the age of 18) were overweight and 13% were found to be obese. Like many other countries obesity is growing at an alarming rate in Saudi adult and youth population [1-4].
Obesity is considered to be a high risk factor for many serious illness and deaths around the globe. If obesity is not controlled, it can eventually lead to serious health problems across the globe, such as hypertension, heart diseases, and T2DM to name just a few. According to the International Diabetes Federation there are 387 million people who have diabetes out of which 37 million live in MENA (Middle East and North Africa Region) region. According to the recent studies individuals who are diagnosed with diabetes spend tenfold more in healthcare expenses ($3686) as compared to the people without diabetes ($380) [5].
For years many home remedies and natural therapies have been used to control diabetes. According to earlier studies vinegar improved sensitivity to insulin in diabetes II patients with high carbohydrate meal [6] and fasting glucose concentrations in diabetic patients [7]. In a similar type of study (unpublished observation) we [1] gave two table spoons of natural apple cider vinegar ten minutes before breakfast and saw a dramatic reduction in the blood sugar levels of up to 28.9% in T2DM Saudi patients of Hail region as compared to the sugar levels (2 hours post breakfast) in same patients without apple cider [1].
Since T2DM is prevalent among adult Saudi population [1,2,8] we decided to analyze if there is any correlation between the inheritance of ABO (A, B, AB, and O) and Rhesus antigen (Rh+ and Rh-ve) blood group distribution in normal adult male (control) Saudi population as compared to the male T2DM patients.
We inherit our blood groups from our parents. It is important to know our blood groups before receiving and or donating blood because transfusion of the wrong blood type can be fatal to the recipients.
Genes for ABO antigens are located on chromosome 9 and have three different alleles (A, B and O) that encode different glycosyl-transferases enzymes with specificities to different substrates thus determining our blood types [9], and the Rhesus antigen (D) gene is located on human chromosome 1. According to earlier studies [10] frequencies and the distribution of ABO blood groups tend to vary among individuals of different countries and there are major differences in the distribution of ABO and Rh (D) antigens between individuals living in different countries. Even populations with different ethnic backgrounds tend to show variations in their blood group frequencies. The reason or reasons for these differences in blood group distribution among different populations are not clearly understood.
Study design
Obesity and the family history are believed to be one of the most important factors in the development of T2DM. We have previously shown prevalence of obesity and diabetes in Hail region of Saudi Arabia [1-4] we wanted to further investigate the reason for these alarmingly high rates of child and adult obesity and the development of T2DM in Saudi Arabia. Recent studies [11] suggest a possible role of ABO and Rh blood groups in the development of diabetes. To date no such studies have been performed in Saudi Arabia. Therefore in this study we investigated the relationship between the inheritance of ABO and Rh blood group antigens and the development of diabetes II among the Saudi male population.
For this study no animal or human samples were utilized. Only T2DM patient’s family history and blood test results on HbA1c analysis and the blood group analysis test results were collected from local diabetes clinics for this study.
Hyperglycemia and high fasting sugar levels were used as the major criteria for diagnosis of T2DM and patient selection. Consistent high HbA1c levels (above 6.5) were considered as the main criteria for selecting the patients for this study. The study plans were submitted and approved by the Ethical Review Committee at College of Medicine, University of Hail.
Methods
A community survey was done and a questionnaire was used and randomly distributed to analyze the prevalence of diabetes among male and female members of the Hail community. We also analyzed the ABO blood group distribution data of 490 controls (non-diabetic) and 544 T2DM who were admitted to the diabetes clinic in King Khaled Hospital in Hail Saudi Arabia between, the years 2008-2015. Out of 544 patients 288 (52.9%) were females and 256 (47%) were males. We recorded the age, gender and HbA1c levels of diabetes patients. Additionally we recorded blood pressure levels and the blood group types of these patients. Blood group data was collected by my IVth year students Ibrahim Hamad Al-Wakid, Abdul Rahman and Dr. Maram Nasser, Dr. Ashjan Muhammad Almhanna, and Dr. Mnieaam Alduejuieman from the local diabetic clinic in King Khaled hospital with the permission of the unit head nurse in charge at the clinic.
Results
Community survey of prevalence of diabetes in Saudi youth and adult population
Since obesity [3] and the cases of T2DM are on the rise in Saudi population (Farshori et al., 2012a) we randomly distributed a questionnaire among educated college youths (average age 18.25 yrs) and the adult non college educated community members (average age 28.15 yrs) and their responses were recorded. Analysis of our community survey revealed that as compared to the college educated youth’s (n= 100) T2DM was more prevalent in the adult community (n= 100). According to this random community survey only 5.5% of educated youth were diabetics as compared to the non college going adult community members where 27.5% community members were found to be T2DM positive (Figure 1).
Figure 1. A community survey of prevalence of T2DM among Saudi youths and the adult community
Patient Age and HbA1c levels
Since diabetes was more prevalent among the Saudi male adults we decided to further investigate the Hb1Ac levels and the blood group distribution among T2DM patients that registered at the King Khaled Hospital in Hail. Average age of our female patients was 45.9 yrs and for male patients it was 49.3 yrs. According to the records male patients had 36% lower HbA1c measurements (8.15 mmol/ L) as compared to the female patients average HbA1c measurements (12.6 mmol/ L) (Table 1). The significance of higher HbA1c values in female patients is not clearly understood.
Gender |
Average Age |
HbA1C levels of T2DM patients |
Female |
45.9 yrs |
12.62 mmol/L |
Male |
49.3 yrs |
8.15 mmol/L |
Table1. Average age and Hb1AC levels among the T2DM patients.
Recently there has been a lot of debate about the importance of diet [12,13] and importance of blood group antigens and their association in causing certain diseases [11]. Since diabetes is also prevalent in Saudi Arabia, we decided to investigate the frequency of distribution of ABO and Rhesus (Rh) antigens among the T2DM patients and the non diabetic (control) population (Figure 2a) of Hail region in Saudi Arabia. We surveyed local non diabetic (control) population ((n=490) among which 42.2% were males and 57.8% were females (Figure 2a). We also analyzed the data of 342 T2DM male and female patients (who registered at King Khalid Hospital). 37.4% of the patients we surveyed were males and 62.6% were females (Figure 2b).
Figure 2. (a) Non diabetic and the diabetic (b) population of Hail region
Frequency of Rh blood groups in control and non diabetic population
Next we determined the frequencies of ABO and Rh blood group distribution in control adult Saudi population of Hail region and compared it with the distribution of ABO and Rh antigens in T2DM patients. Data analysis shows 10.6 % of the control population was Rh- and 89.4% were Rh+ (Figure 3a). Among diabetic male patients only 3.13% were found to be Rh- while 96.8% were Rh +. These results show a 3.4 fold reduction in T2DM cases among the Rh- individuals (Figure 3b). The reason for this dramatic yet significant reduction in diabetes patients is under investigation.
Figure 3. Distribution of the Rhesus antigen (Rh+) in control (3a) and T2DM patients (3b) of Hail region
Distribution of ABO antigens in non diabetic (Control) male population
Out of 89.4% ABO positive individual’s (Figure 3a) O positive was the most prevalent blood group (42.9% and 3.4% O-), while AB was the least prevalent blood group (4.3% were AB+ and 0.97% A-) in non diabetic control population. Further analysis of our control population data revealed 20.8% were A+ and 2.9% were found to be A-. Similarly 21.2 % were found to be to be B+ and 3.4% were found to be B- (Figure 4).
Distribution of ABO a2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
Next we decided to analyze the distribution of ABO and Rh antigens among T2DM male patients. Like control population O blood group was the most prevalent among these patients. 39.1 % of T2DM patients were O+ and 0.78% were O-. However the percentage of diabetes patients with O+ blood type was slightly lower (39.1%) than the control (about 43%) group (Figures 4 & 5). Like control population, B+ blood group was the second most prevalent group in male T2DM patients. However we found a significantly high frequency of B+ antigens among T2DM patients(30.5%), (Figure 5) as compared to 21.2 % B+ individuals in the control population (Figure 4). Further data analysis showed about similar frequencies of distribution of A+ blood group in controls (20.8%) and in T2DM patients (22.65%). Like control population, AB was the least frequent blood group (4.7 %) among male T2DM patients. In summary our results clearly show that O+ is the most prevalent and AB+ is the least frequently distributed blood group in control and among the T2DM patients in Hail region of Saudi Arabia. However B+ blood type seems to show significantly higher frequency of distribution among the male T2DM patients (Figure 5).
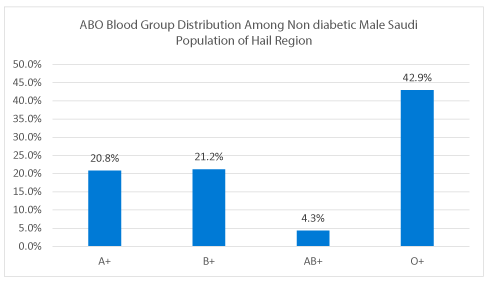
Figure 4. Distribution of ABO group in control non diabetic male population in the Hail region
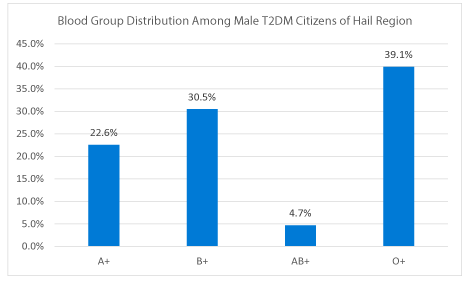
Figure 5. Distribution of ABO group in male T2DM patients in the Hail region
Percent change in ABO antigen expression in male T2DM patients as compared to the control non diabetic population of Hail region
Finally we looked at the percent change in the ABO and Rh antigen expressions in Diabetes II patients in comparison to the control population. If we consider the distribution of control blood types (A, B, AB, and O) as 100% and then compare it to the frequencies of expression of these blood types in diabetic patients we see a statistically significant increase of about 44% in blood type B+ expression in T2DM patients as compared to the control group (Figure 6). Our results also show a slight decrease in the expression of the O+ blood type (a 9% reduction) as compared to the non diabetic control group (Figure 6).
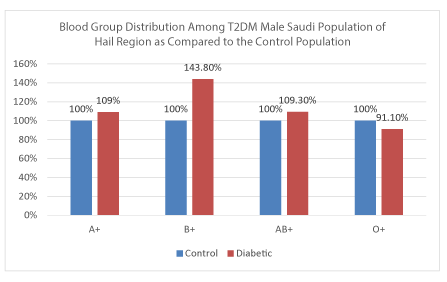
Figure 6. Percent change in ABO antigen expression in male T2DM patients as compared to the control non diabetic population of Hail region
Statistical analysis of ABO and Rh distribution in control and T2DM patients
Statistical analysis of our data using t-test calculator showed no significant difference in the frequency of distribution of A+ blood type (male and female) between non diabetic control and the T2DM patients (the t value was -2.80 and the p-value was 0.106 at p ˂ 0.10). Next we compared the frequency of distribution of B+ blood group. The t value was -3.009 and the p value was .094. The p value was significantly different (p- ˂ .10) in diabetics (39.1% B+) as compared to the controls (21.2% B+). These results suggest high frequency of distribution of B+ blood group among the T2DM patients as compared to the control group. However these results were not significant at p ˂ .05. Like A+ blood type our data shows no significant difference (statistically not significantly different) in the distribution of AB+ blood type between control and the T2DM patients. The t value was -1.05 and the p-value was .403. Therefore according to our results AB+ distribution was not significantly different at p- ˂ .10. Next we looked at the distribution of O+ blood types between the controls and the T2DM patients. Our results show distribution of O+ to be comparatively lower in T2DM patients (t-value 3.43 and the p value .0754) at p- ˂ .10.
Finally we compared the presence or absence of Rh factor between the control and the T2DM patients. Our results show 10.6% of the control non diabetic population to be Rh-negative, however among the diabetics only 3.13% patients were Rh negative (t value 5.75% and the p value was .028). These results were significant at p- ˂ .05. Therefore in our study collectively Rh- is expressed in fewer of the male T2DM patients (3.13% Rh-) as compared to the non diabetic control group (10.6% Rh-).
In conclusion statistical analysis of our data shows a significant increase in the distribution of B+ blood type (Figure 5) and a significant decrease in number of T2DM patients with Rh- (absence of Rhesus antigen) blood type (Figure 3b). Significance of this significant reduction in the percentage of Rh negative patients among the T2DM male patients is not clearly understood and is currently under investigation.
Discussion
ABO blood group antigens play an important role during organ transplantation and blood transfusion. A small error in matching the donor and recipients blood type can be fatal for the recipients. Therefore, it is important to know our blood group before blood transfusion, surgery or an organ transplant. Karl Landsteiner a pathologist and a 1930, Nobel Prize winner for Physiology and Medicine discovered the ABO blood groups at University of Vienna in 1900s.
Blood group antigens commonly known as ABO and Rh antigens are genetically inherited from our parents. Different populations tend to show differences in the distribution of these ABO and Rh antigens [14]. For example in Saudi Arabia 24% people were A antigen positive, 17% were B antigen positive, 4% were AB antigen positive and 52% were O blood type [15], as compared to the USA population where 41% population was A antigen positive, 9% B antigen positive, 4% was A and B antigen positive (AB blood type), and 46% were O blood type [10,16]. Significance of these differences in ABO blood group distribution between different populations is not clearly understood. However it is believed that individuals with certain blood types are more prone to get certain diseases. For example ABO blood antigens and Rhesus factors have previously been shown to be associated with the risk of stroke [17] and the coronary heart disease [18]. In some studies an increased frequency of diabetes mellitus was found in individuals with blood type B and a decreased frequency in people with AB blood type [19]. Recently, Bener and Yousafz suggested similar findings of high frequency of B blood group among diabetic patients additionally they found O blood type to be significantly less common [20]. However according to other studies blood group O and AB were more common in diabetes II patients (Dali Sahi et al., 2011). In another study O- and A+ blood type were significantly higher in diabetes patients as compared to the non diabetic controls [21]. Since, the data on association of the blood groups (ABO and Rhesus antigens) with diabetes is contradictory and since to our knowledge no such study has been done in Saudi Arabia. We decided to study a possible association of blood groups with the development of T2DM in male Saudi patients.
Our community survey revealed a high prevalence of T2DM among non college educated adult population. The interesting part of this survey was a low number of T2DM cases among the educated youth (Figure 1). These findings suggest that today’s youth, being the digital generation with unrestricted availability of health related data on internet are very well informed about T2DM and its consequences. We believe today’s youth are well aware of importance of balance diet and exercise in controlling obesity and T2DM. More studies with larger sample size need to be done to confirm these findings.
Next we studied the distribution of ABO and Rh antigens among non diabetic control population of Hail region. According to Bashwari et al., 2001, in eastern region of Saudi Arabia 48% individuals were O+, 24+ A+, 17% B+ and only 4% were AB+ [15]. According to this study O+ was the most prevalent and AB+ was the least prevalent group in Saudi Arabia. Our data shows the similar findings in non diabetic control population. Since Diabetes is rising rapidly in Saudi population and to our knowledge no such studies have been done in Saudi population, we decided to take this study to the next level and study the distribution of ABO and Rh (D) blood groups among T2DM patients of Hail region of Saudi Arabia and compare it with the distribution of ABO and Rh (D) antigens in control non diabetic population.
Statistically we found no significant difference in the distribution of A+ blood type (male and female) or AB blood type between the male non diabetic controls and the male T2DM patients (Figures 4-6). However we found a significant increase in B+ blood type among the T2DM patients as compared to the control group. Our results also show a small reduction in percent distribution of O+ (Figures 5 and 6) among the T2DM male population (at p- ˂ .10). Finally we analyzed the expression of or absence of Rh factor between the control and the T2DM patients. We found 10.6% of control non diabetic population to be Rh negative and 89.4% to be Rh+ (Figure 3a), however among the diabetics only 3.13% patients were Rh-negative and 96.8% were Rh+ (Figure 3b). These results were significant at p- ˂ .05. Therefore in this study fewer of the male T2DM patients were Rh- (3.13%) as compared to the non diabetic control group (10.6% Rh).
In conclusion statistical analysis of our data shows a significant increase in the distribution of B+ blood type and a significant decrease in the distribution of Rh- (absence of Rhesus antigen) among Saudi male T2DM patients of Hail region. Since this was a small study a larger studies needs to be done to further investigate the association between blood group inheritance and the development of T2DM.
Study limitations
This study was conducted with a small number of subjects available in Hail city. In total 490 non diabetic controls (283 females and 207 males) and 342 T2DM patients (214 female and 128 male patients) were available. For each T2DM patient we collected only the first reading of HbA1c levels available.
Conclusions
Our study suggests that people with B+ blood tend to show least resistance to T2DM with high frequency of distribution, the t value was -3.009 and the p value was .094 at p- ˂ .10, and the O+ blood type individuals show some resistance (low frequency of distribution) in diabetes type II patients (t-value 3.43 and the p value .0754) at p- ˂ .10. Therefore frequency of distribution of B+ blood group is significantly higher in male T2DM patients. Our results also show more than 3 fold decrease in Rh- individuals among diabetes patients. Significance of this decrease in Rh- individuals among diabetics as compared to the control population is not clear at this time. Larger clinical studies need to be done to further investigate the reason why as compared to control population O+ blood group tend to show lower incidences and B+ high incidences of T2DM among Saudi male patients.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Rida Khan for editorial corrections of the manuscript and my students Ibrahim Hamad Al-Wakid, Abdul Rahman, Dr. Maram Nasser, Dr. Ashjan Muhammad Almhanna, and Dr. Mnieaam Alduejuieman for collecting the blood group data from the local diabetic clinic in King Khaled hospital. The authors would also like to thank 3rd year medical student Ibrahim Hamad Alwakid Abdul Rahman Ali Abdul Rahman for helping us with the graphics. Last but not least authors would like to thank Ibad Farshori for helping us with the statistical analysis of our data.
References
- Farshori MPQ, Al-Rudan S, Al-Nasser H, Alshammari R (2012a) Effects of Apple Cider Vinegar on Fasting Blood sugar levels of Diabetic patients and to analyze the effects of Vinegar on Human enzyme amylase. GCC8 international conference of Medical students Masqat OmanAbs # 1262.
- Farshori MPQ, Al-Hazmi A, A-Alsadery H, Aljaza TS, Alazmi SM (2012b) Inheritance of PTC taster gene among obese people of Hail city. GCC8 international conference of Medical students in Masqat Oman, 2012c. Abs # 1267.
- Farshori MPQ, Altamimi N, Alsadery HA, Aljaza TS, Alazmi SM, et al. (2015) Rapidly rising rates of adult obesity and child obesity in schools of Hail region of Saudi Arabia: A comparative analysis. Integr Obesity Diabetes 1: 163-166.
- Farshori MPQ, Altamimi N, Aljamany M, Alafnan A, Alhazmi A (2014) Alarmingly High Rates Of Child Obesity In Saudi Arabia. A Possible Link Between Obesity And Inheritance Of Phenylthio Carbamide Gene (PTC). Presented at ICO on March 17 (2014) in Kualalampur Malaysia.
- Alhowaish AK (2013) Economic costs of diabetes in Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med 20: 1-7. [Crossref]
- Johnston CS, Kim CM, Buller AJ (2004) Vinegar improves insulin sensitivity to a high-carbohydrate meal in subjects with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: 281-282. [Crossref]
- White AM, Johnston CS (2007) Vinegar ingestion at bedtime moderates waking glucose concentrations in adults with well-controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30: 2814-2815. [Crossref]
- Alqurashi KA, Aljabri KS, Bokhari SA (2011) Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in a Saudi community. Ann Saudi Med 31: 19-23. [Crossref]
- Reid ME, Mohandas N (2004) Red blood cell blood group antigens: structure and function. Semin Hematol 41: 93-117. [Crossref]
- Chandrika R, Jayaprakash S (2014) Frequency of ABO and Rhesus (D) blood groups in dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka. A study from rural tertiary care teaching hospital in south india. NUJHS 4: 5761.
- Fagherazzi G, Gusto G, Clavel-Chapelon F, Balkau B, Bonnet F (2015) ABO and Rhesus blood groups and risk of type 2 diabetes: evidence from the large E3N cohort study. Diabetologia. 58: 519-522. [Crossref]
- Du Q, Wang Q, Fan H, Wang J, Liu X, et al. (2016) Dietary cholesterol promotes AOM-induced colorectal cancer through activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem Pharmacol 105: 42-54. [Crossref]
- Lozano I, Van der Werf R, Bietiger W, Seyfritz E, Peronet C, et al. (2016) High-fructose and high-fat diet-induced disorders in rats: impact on diabetes risk, hepatic and vascular complications. Nutr Metab (Lond) 13: 15. [Crossref]
- Behra R, Joshi YR (2013) Distribution of ABO blood group and RH (D) factor in western Rajasthan. National J Medical Res 3: 73-75.
- Bashwari LA, Al-Mulhim AA, Ahmad MS, Ahmed MA (2001) Frequency of ABO blood groups in the Eastern region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 22: 1008-1012. [Crossref]
- Frances TF (2002) Blood groups (ABO groups). In: common laboratory and diagnostic tests. (edn. 3rd), Philadelphia: Lippincott, USA 19-50.
- Zakai NA, Judd SE, Alexander K, McClure LA, Kissela BM, et al. (2014) ABO blood type and stroke risk: the REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke Study. J Thromb Haemost 12: 564-570. [Crossref]
- He M, Wolpin B, Rexrode K, Manson JE, Rimm E, et al. (2012) ABO blood group and risk of coronary heart disease in two prospective cohort studies. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32: 2314-2320. [Crossref]
- Buckwalter JA (1964) Diabetes Mellitus and the Blood Groups. Diabetes 13: 164-168. [Crossref]
- Bener A, Yousafzai MT (2014) The distribution of the ABO blood groups among diabetes mellitus patients in Qatar. Niger J Clin Pract 17: 565-568. [Crossref]
- Okon UA, Antai AB, Osim EE, Ita SO (2008) The relative incidence of diabetes mellitus in ABO /Rhesus blood groups in south eastern Nigeria. Niger J Physiol Sci 23: 1-3. [Crossref]






