Background: A facial nerve palsy combined with a parotid mass commonly suggests malignancy. A few cases have be reported in which facial palsy was due to parotid benign lesions such as abscess or benign tumors.
Presentation of case: We experienced facial nerve palsy due to a parotid abscess resulting from Warthin’s tumor. At first, the inflammation of this parotid lesion could be suppressed by fine needle aspiration and the administration of antibiotics. These treatments could improve the facial nerve palsy. Cytological examination led to a diagnosis of a benign tumor. Second, we performed parotid surfacial lobectomy of this lesion.
Conclusion: Cases of recovery from facial nerve palsy with parotid lesions should be kept in mind for the differential diagnosis given the possibility of parotid benign lesions such as abscess or benign tumors.
facial nerve palsy, parotid absces, Warthin’s tumor
Facial nerve palsy is associated with a parotid mass suggests malignancy. However, a few cases of benign lesions of the gland causing facial nerve paralysis have been reported. Such lesions included benign tumors (pleomorphic adenomas, Warthin’s tumor, cyst, etc. and infection (suppurative parotitis, parotid abscesses) [1-3]. We experienced a case of facial nerve palsy due to a parotid abscess resulting from Warthin’s tumor. This case report presents the clinical findings, imaging examination, treatment and postoperative progress. Moreover, we discuss the treatment methods and mechanisms of facial nerve palsy due to benign parotid lesions with references to the literature.
This patient was an 81-year-old Japanese man who had already been diagnosed with a benign parotid tumor and received follow-up by previous doctors. He visited other doctors with a 5-day history of left facial palsy and pain with more parotid swelling and received oral antibiotics. However, the parotid pain and swelling did not improve and the left facial palsy continued.
He then consulted the first author. His past history included diabetes mellitus, cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. In the initial findings, he had left parotid swelling and facial paralysis. In the facial paralysis grade, his Yanagihara’s score was 26/40. Echo and MRI showed multiple cystic lesions (Figure 2). Fine needle aspiration (FNA) showed a 12cc purulent pus. Microbial cultivation and cytologic examination of the FNA sample showed no growth of bacteria and no malignant cells. In the blood examination, the white blood cells and C-reactive protein were 10,700/μl (normal range: 4000-8000//μl ) and 0.9 mg/dl(normal range:0-0.3 mg/dl), respectively .
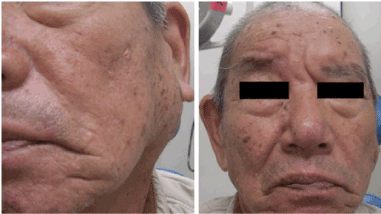
Figure 1. At the first physical examination, a left parotid gland swelling(Left) and facial paralysis(Right) were found.
From the above clinical findings and examination, we considered that this case could be facial nerve palsy due to a parotid abscess resulting from a benign parotid tumor. Therefore, we administered antibiotics (intravenous piperacillin 2g/day X 5days, oral amoxillin 750mg/day X 9 days) to suppress the inflammation. The parotid swelling and pain decreased at 5days after starting the antibiotics. In the blood examination, white blood cells (5,300 /μl) and C-reactive protein (0.3 mg/dl) were within the normal range. Moreover, Yanagihara’s score for the facial nerve palsy improved from 26/40 to 34/40 on (Figure 2) but the recovery was not complete.
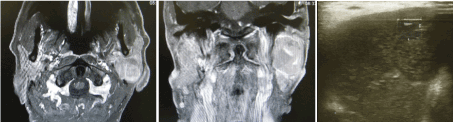
Figure 2. MRI (T1 WI with enhancement)and echo revealed a multiple and homogenic cystic lesion (long diameter: 40mm).
A functional area of the temporal branches of the facial nerve showed continued paralysis.
The score of his facial nerve palsy remained the same for two months after the administration of antibiotics. Therefore, we considered that our case would benefit from surgical treatment of the parotid abscess to protect recurrent infection and rule out malignancy by histopathologic examination, and performed parotid surfacial lobectomy. In the operative findings、the parotid tumor showed adhesion to a scar surroundings a main trunk of the facial nerve.
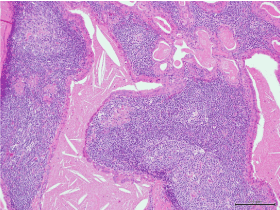
Nevertheless, we were able to preserve the main trunk and branches of the facial nerve without injury. The resected specimen was 40mm in diameter and contained multiple cysts with fluid of muddy brown back. The histopathologic examination could conform warthin’s tumors as benign tumor (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Diagnosis of histologic examination (HE staining) was Warthin’s tumors. This parotid tumor showed well-defined cysts and epithelial cells with lymphoid follicules and papillae proliferating toward the lumen. In a part of the cyst walls ciliated epithelium and squamous metaplasia were found.
Cases of facial nerve palsy due to parotid gland pathology are usually associated with malignancy, In contract, Its occurrence as a complication of parotid is extremely rare [4,5]. Orhan and Primuharasa Putra [6,7] suggested that facial nerve palsy with the parotid abscess would be a condition seen mainly in elderly, diabetic and immunocompromised patients as presented in our case. Past history of our patient had diabetes mellitus, cerebaral infarction and myocardial infarction. Some hospitals recommended that management of parotitis complicated by facial paralysis should initially be conservative with antibiotics and most case reported recovery of the facial nerve after resolution of the acute in flammatory process [4,5,8] .Takenagawa and Grosheva [9,10] presented cases of facial nerve palsy due to warthin tumors. Their cases showed parotid abscess with Warthin tumors and underwent parotidectomy after suppressing inflammation by administration of antibiotics as our cases. Takenaga [9] described that facial nerve palsy could not improve by antibiotics, therefore, they suspected possibility of malignant parotid tumor and perform operation. Kawata [11] recommended that the indications for surgical treatment of parotid abscess would be to protect recent infection and need rule out malignancy by histopathologic examination. Benign parotid as well as parotid abscess rarely causes facial nerve palsy [2]. In our case, facial nerve palsy could slightly improve by antibiotics, but not complete recovery. We could not rule out malignancy perfectly. Our patient was elderly, diabetic and immunocompromised condition. To protect repeating parotid abscess and conform histopathologic findings whether parotid tumor is benign or malignancy, we performed parotid surfacial lobectomy. The postoperative histopathologic diagnosis was Warthin’s tumor.
Concerning the mechanisms of facial nerve palsy due to benign parotid lesion, Marini [12] suggested4mechanisms of facial nerve palsy due to benign parotid tumors as follows;
(1) compression or stretching of the nerve by enlargement of the mass; (2) direct extension of the mass into the fallopian aqueduct via the stylomastoid foramen; (3) kinking of the nerve tissue as it enters the firm parotid fascia; (4) impairment of the facial nerve function caused by acute infection, thrombosis of perineural vessels, edema formation or direct neurotoxic effects due to inflammatory mediators.
In conclusion, cases of recovery of the facial nerve palsy with parotid lesions should be kept in mind given the possibility of parotid benign lesions such as abscess or benign tumors.
Author’s contributions
Takeshi Kusunoki MD: diagnosis and therapy, composition of this case report
Hirotomo Honma MD: therapy
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
Yoshinobu Kidokoro MD: therapy
Aya Yanai MD: therapy
Satoshi Hara MD: therapy
Yuko Kobayashi MD: therapy
Miri Tou MD: therapy
Ryo Wada MD: Pathological diagnosis
Katsuhisa Ikeda MD: composition of this case report
Consent for publication: We confirmed a patient’s anonymity and a consent for publication on clinical findings, image examinations and pathological examinations was obtained for this case report.
Availability of data and materials: NA
Competing interests: The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Funding: NA
Acknowledgements: The authors thank Mr.Brent Bell for checking English of the manuscript.
- Hajiioannou JK, Florou, Kousoulis P, Kretzas D, Moshovakis E (2013) Reversible facial nerve palsy due to parotid abscess. Int J Surg Case Rep. 4: 1021-1024. [Crossref]
- DeLozier HL, Spinella MJ, Johnson GD (1989) Facial nerve paralysis with benign parotid masses. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 98: 644-647. [Crossref]
- Jecker P, Hartwein J (1993) [Facial paralysis in benign parotid tumor: case report and review of the literature]. Laryngorhinootologie 72: 204-206. [Crossref]
- Kristensen RN, Hahn CH (2012) Facial nerve palsy caused by parotid gland abscess. J Laryngol Otol 126: 322-324. [Crossref]
- Noorizan Y, Chew YK, Khir A, Brito-Mutunayagam S (2009) Parotid abscess: an unusual cause of facial nerve palsy. Med J Malaysia 64: 172-173. [Crossref]
- Orhan KS, Demirel T, Kocasoy-Orhan E, Yenigül K (2008) Facial paralysis due to an occult parotid abscess. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 18: 115-117. [Crossref]
- Sabir Husin Athar PP, Yahya Z, Mat Baki M, Abdullah A (2009) Facial nerve paralysis: a rare complication of parotid abscess. Malays J Med Sci 16: 38-39. [Crossref]
- Bahna M, Canalis RF (1980) Necrotizing fasciitis. (Streptococcal gangrene) of the face. Report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Otolaryngol 106: 648-651. [Crossref]
- Takenaga F, Ohkubo M, Mori T, Ohbuchi T, Houchi N, et al. (2012) Warthin’s tumor associated with facial nerve palsy. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (Tokyo) 84: 49-53.
- Grosheva M, Ortmann M, Beutner D (2010) [Facial nerve palsy due to a benign parotid gland tumor]. HNO 58: 1197-1198, 1200. [Crossref]
- Kawata R (2015) Salivary absess.Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (Tokyo) 87: 130-133.
- Marioni G, de Filippis C, Gaio E, Iaderosa GA, Staffieri A (2003) Facial nerve paralysis secondary to Warthin's tumour of the parotid gland. J Laryngol Otol 117: 511-513. [Crossref]